Hello friends, in today’s article, we are going to discuss stems. What is a plant’s stem? We will study how it is made and much more. So, without wasting any time, let’s start.
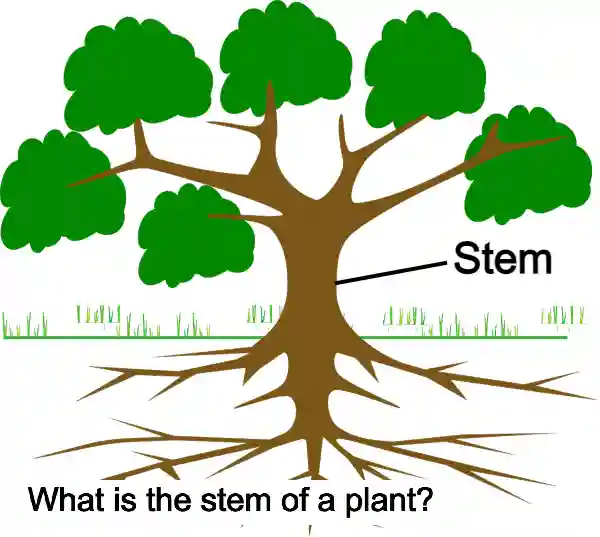
What is the Stem of a plant?
Except for the root, leaf, flower, and fruit, the part that remains is called the Stem.
How is the Stem formed of a plant?
The plant is formed from one or more seeds, and on top of this seed, there are two coverings called seed cover or seed coat. Inside this seed, an embryo is found, and in this embryo, there are two structures of cells: a plumule and a radicle.
When the seed is put in the soil, the mineral elements and water present in the soil cause the embryo to develop, and the plumule and radicle later form the stem, and the Radicle forms the root.
Now you know that the Stem is formed from the plumule present in the embryo. When this Plumule is formed from a small stem in the beginning, that small Stem is called a pubescent stem. Now, this Stem gradually grows and grows, and branches, leaves, and flowers emerge from this Stem, and these flowers later become fruits.
We are talking about the Stem. There are some swollen areas in the Stem, which are called nodes. You must have seen this in sugarcane. The region between two nodes is called the internode.
The bud is found at this node and also on the top part of the Stem. The bud on the top part is called the apical bud, and the bud found on the node or axis is called the axillary bud. Both buds are a type of meristematic tissue.
What is meristematic tissue?
Cells that divide continuously are called meristematic tissue.
Now, the apical bud keeps on dividing, and the length of the stem increases. This means this bud is working to increase the length of the Stem. However, the axillary bud divides to form a leaf, and the stem-like structure in the center of the leaf is called the midrib.
The loose green part of the leaf is called the lamina or leaf blade. This star gradually gets destroyed. When the lamina is destroyed, the midrib continues to grow further, and a structure called a branch is formed.
Now, there are nodes and internodes on this branch. There is an axillary bud at the node and an apical bud at the apex, which divides and enlarges the apical part. But which is axillary bud? It is of two types: leaf bud and flower bud. The leaf bud divides to form a leaf, and the floral bud produces a flower.
Now, you must have understood how stem formation takes place.
What is the function of the Stem of a plant?
The function of the Stem of a plant –
The Stem mainly spreads the branches and serves to maintain the leaves, flowers, and fruits; not only this, but it also conducts water, mineral elements, and photosynthetic substances through the xylem and phloem. But some stems store food, give support, and also do the work of vegetative propagation.
How many types of stems are there in a plant?
There are three types of stems, depending on the condition of the land.
- Underground Stem
- Aerial Stem
- Semi-aerial Stem
What is the underground Stem of a plant?
Underground stems are those found inside the soil, such as those of potatoes, turmeric, and ginger.
What is the aerial Stem of a plant?
The Stem, which is completely situated in the air on the ground, is called the aerial Stem. Such a stem has branches, leaves, flowers, and fruits like – roses, hawthorn, grapes, etc.
What is a semi-aerial stem of a plant?
Those stems have some part inside the ground and some part outside the ground in the air, so such stems are called semi-aerial stems—for example – grass, hyacinth, strawberry, pistia, etc.
Modification of the Stem of a plant
We have seen in stem function that some stems store food, and these stems modify themselves to store food. Examples include potato, turmeric,ginger, and zamikand. These items are found underground; hence, they are called underground stems. The zaminkand plant has the longest flower on earth, and the Rafflesia flower is the biggest.

Some stems turn into a curved structure like a spring, which is called a tendril.
You must have seen cucumbers, watermelons, pumpkins, peas, and other plants. These plants support the weak Stem while standing and climbing.
Many such plants have thorns, which are modifications to the Stem. You people must have eaten plums, and if you had seen this plum tree, you would know that it had many sharp thorns. Now, it comes to the question of what these thorns do. See, these thorns protect the plant from hunters (animals).
Example – Citrus, Bougainvillea.
Due to the lack of water in the desert area, the leaves that are there are converted into thorns to reduce the process of transpiration in the plant. Now, the transpiration decreases, but these thorns cannot do photosynthesis, and when there is no photosynthesis, then from where will the food be made? When the food is not made, the plant will dry up, but it does not happen.
This is because the Stem of this plant becomes green and starts working like leaves; that is, in their Stem, chlorophyll and a few fewer stomata are found than in the leaves, which is why the exchange of gases and photosynthesis takes place. The stomata are called lenticels. So much Stem is called Phylloclade. Transpiration from this is 1-3%, while transpiration from leaves is 90-92%.
Examples – Opuntia, Cactus, Euphorbia.
Also, read – What is the function of root?
Some plants, like grass and strawberries, which have stems, crawl on the ground, and at some distance, these stems take out roots and form a plant; in the same way, from this plant, the stems go ahead by crawling, and the roots and plant This is how it goes on. These stems are called semi-aerial stems.
Why are they called semi-aerial stems? Because some parts of their stems are inside the ground, and some are outside the ground, they are in the air.
In these plants, the old plant that is there dies, and the stems that are there keep forming a new plant. That means these stems are saving these plants from extinction.
Examples – Grass, Strawberry, etc.
In mint and jasmine plants, a branch or Stem emerges from the base of the main Stem. It grows in the air for some time and then turns and touches the ground. Where it touches, a plant is formed again. In the same way, this process continues. This means that the Stem is creating new plants.
Some aquatic plants, like Pistia and Eichhornia (hyacinth), have stems that emerge from their base and crawl on the surface of the water. At some distance, these stems form another plant, and then the stems from this plant continue crawling on the surface of the water to create another plant. This process continues, and the number of plants keeps increasing.
So, friends, I hope that you enjoyed the information about the Stem of a plant. If you do, please share it on your social media platforms.
The answers to all the questions below are in the article; you only need to read the complete article.
- What does the Stem of a plant do?
- What is the Stem of a plant?
- What is the node of a plant stem?
- What is the function of the Stem of a plant?
- Where does the majority of stem growth in a plant occur?
Thank you