Hello friends, in this article, we will learn everything about the ribosome’s start without wasting time.
What is the occurrence and location of the ribosome?
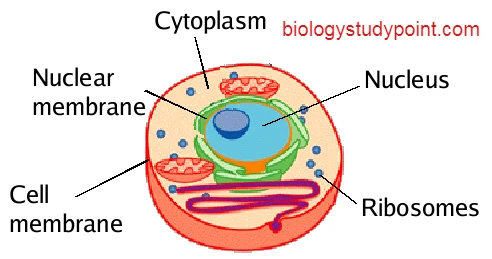
Ribosomes are microscopic granules about 150 to 200 angstroms in diameter. They are found in all living cells, either attached to the outer membrane of the Endoplasmic Reticulum or scattered in the cytoplasm. These are described as protein factories of the cell because they synthesize the protein of the cell.
Who discovered the ribosome?
Ribosomes were first observed by Palade in 1955 under an electron microscope as dense particles.
How many types of ribosomes?
Ribosomes found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes are of different sizes and have different sedimentation rates. Therefore, ribosomes are of the following two types.
Ribosomes are generally oblate spheroidal, measuring 18 nm in bacteria and 20-22 nm in Eukaryotic cells. These occur in 2 categories.
- 70S ribosomes are found in bacteria (prokaryotic cells), mitochondria, and chloroplast.
- 80S Ribosomes found in Eukaryotic cells.
Ultrastructure of Ribosomes
The basic design of both prokaryotic and Eukaryotic chromosomes is the same: a small and a large subunit. The small subunit forms a cap on the large subunit.
What are prokaryotic ribosomes?
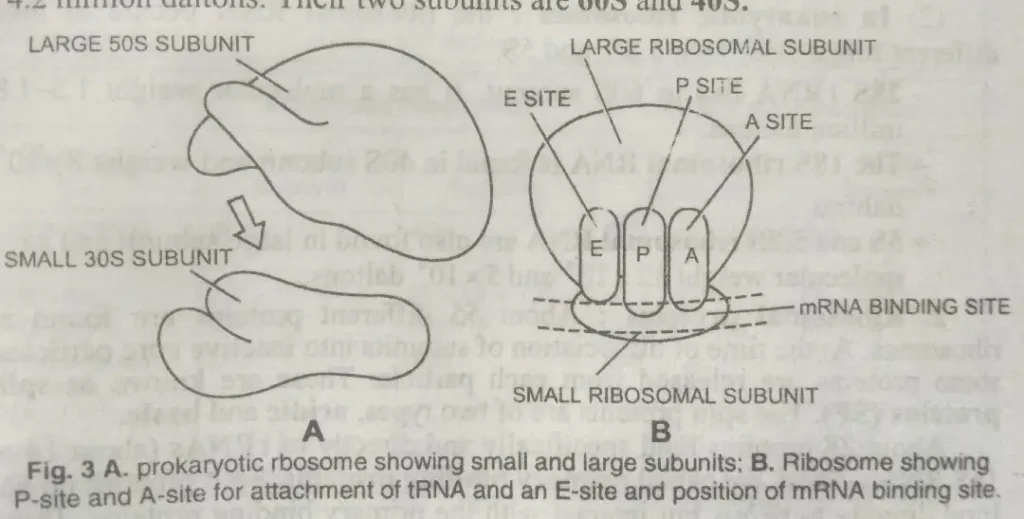
Prokaryotic ribosomes (70S Ribosomes) -Prokaryotes’ ribosomes have a diameter of about 18 nm and a particle weight of 2.8 million Dalton’s. It has two subunits: 50S and 30S. Lake (1985) gave the structure model for prokaryotic ribosomes.
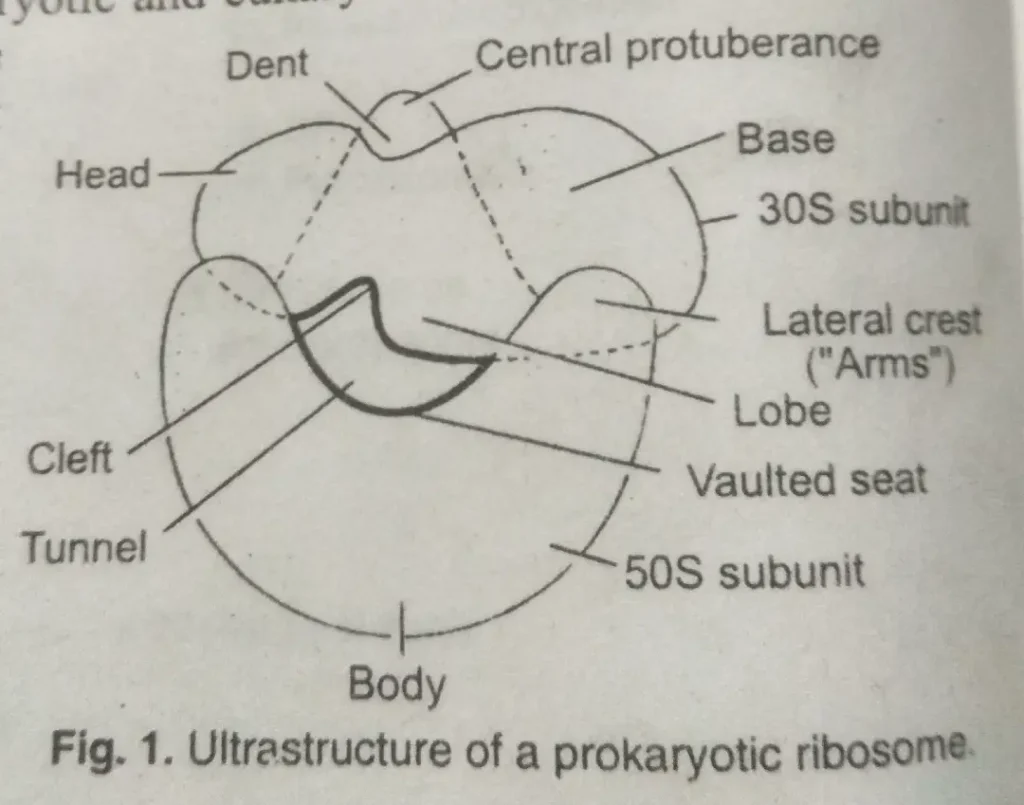
Lake’s model of 70S prokaryotic ribosome
(i) 30S subunit – The small subunit of prokaryotic ribosomes is the 30S. It is asymmetrical and rod-like. It is partially divided into two lobes by a Deep transversal cleft or groove. The smaller segment is called the head, and the larger one is the base. A small outgrowth, called a platform, arises from the base segment.
The particle weight of a 30S subunit is about 1.0 million Dalton. It is formed of one molecule of 16S rRNA and 21 proteins.
(ii) 50S subunit – It is the large subunit. It is more or less Spherical and forms the body. At its flat anterior end are three projections, one central projection, and two lateral projections.
The 50s subunit has a particle weight of 1.8 million Dalton’s. It comprises one molecule of 23s rRNA, one molecule of 5S rRNA, and 34 proteins.
The two subunits are fitted together in a ribosome to form a tunnel. During Protein synthesis, mRNA is threaded through this tunnel.
What is a Eukaryotic ribosome?
Eukaryotic ribosome ( 80S ribosome) –
The 80s ribosome has a diameter of about 20- 22 nm and a particle weight of 4.2 million Dalton’s. The two subunits are the 60S and 40S.
The 60S Subunit weighs about 2.7 million Dalton’s. It contains 28S, 5S, and 5.8S rRNA and about forty different proteins. It has a broad anterior flat surface and three projections.
The 40S subunit weighs about 1.5-1.8 million Dalton. It has 1.8 rRNA and 30 different polypeptides.
Attachment of the ribosome to the Endoplasmic Reticulum
The large subunit gets attached to the Endoplasmic reticulum membrane and bears two slots for two molecules of transfer RNA. These are P-site (peptidyl or donor site) and A-site (aminoacyl or acceptor site).
The aminoacyl tRNA complex (AA-tRNA) is attached to the acceptor site, and the tRNA-carrying peptide chain is connected to the peptidyl or Donor site. The smaller subunit receives the messenger RNA. The cleft separating the two subunits lies parallel and remains attached to the membrane of the Endoplasmic reticulum.
Chemical composition of Ribosome
Ribosomes are formed of approximately equal amounts of RNA and proteins. Proteins form the Periphery, and RNA lies in the interior, remaining intertwined between the two subunits.
- Ribosomal RNA –
(i) In prokaryotic ribosome –
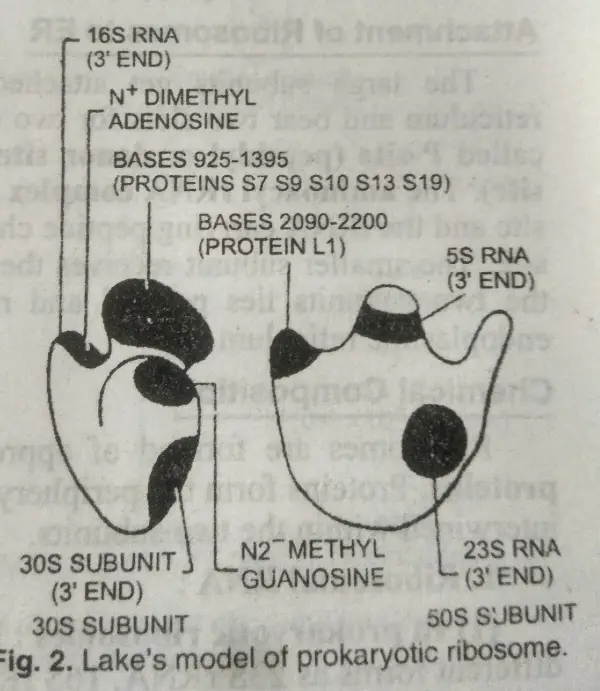
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Occurs in three e different forms: 23S rRNA, 16S rRNA, and 5S rRNA.
- 23S rRNA occurs in the 50S subunit. The molecular weight is 1.2 million (i.e., 1.2×106) Dalton’s and contains about 3200 nucleotides.
- 16S rRNA Line in 30s subunit. It has a molecular weight of .6×106 Dalton’s and contains about 1600 nucleotides.
- 5S rRNA also lies in a large subunit. It has a molecular weight of 3.2X104 Dalton, having 120 nucleotides.
(ii) In Eukaryotic ribosome –
The ribosomal RNA occurs in 28S, 18S, 5.8S, and 5S.
- 28S rRNA lies in 60s subunit. It has a molecular Weight of 1.5 – 1.8 million Dalton.
- The 18S ribosomal RNA is found in 40S subunits and weighs .8×106 daltons.
- 5S and 5.8S ribosomal RNA are also found in large subunits with molecular weights of 3.2x 104 and 5×104 Dalton.
2. Ribosomal proteins –
Ribosomes contain about 55 different proteins. When subunits are dissociated into inactive core particles, some proteins are released from each particle. These are known as split proteins (SP). There are two types of split proteins: acidic and basic.
About 28 proteins bind specifically and directly to sRNAs (14 to 16S RNA). These are called primary binding proteins. Split proteins do not bind directly to rRNA but interact with the primary binding proteins. These are also called secondary binding proteins.
Biogenesis of ribosome
The ribosome in bacteria is found inside the cytoplasm because of the absence of nucleolus. The ribosomal RNA is coded from the specific cistrons of the genome.
However, the process is complicated in eukaryotes, and ribosomal RNA is synthesized in the nucleolus. In the beginning, 45S RNA is formed from the nucleolar organizer region of the chromosome.
This 45S RNA is a Precursor of both 28S and 18S sRNAs. The figure illustrates the process of converting 45S RNA into 28S and 18S ribosomal RNA.
A symbol in the nucleolus represents protein syntheses in the cytoplasm. They are associated with RNA to form ribonucleoprotein particles (RNP).
Difference between ribosome and lysosome
Ribosomes are granules of protein and RNA present in the cytoplasm. They are often attached to the endoplasmic reticulum, where protein synthesis occurs.
Lysosomes are cytoplasmic organelles of cells that contain digestive enzymes for intracellular digestion of bacteria and other foreign bodies, which enter the cells through phagocytosis or PinOcytosis. They may cause cell destruction.
What are Mitochondrial ribosomes (mt, ribosome)?
Mitochondria ribosomes occur freely in the mitochondrial matrix or are attached to cristae membranes. The sedimentation coefficient of mitochondrial ribosomes in yeast fungi, Protozoans, and higher plants varies from the 70S to the 80S.
The mitoribosomes in animal cell mitochondria have a 50-80S Sedimentation coefficient. They also have chondral Subunits and contain only two types of ribosomal RNA.
In animal mitochondria, the large subunit contains 16S to 18S rRNA, and small subunits have 12S to 13S RNA.
Mitochondrial ribosome synthesis of mitochondrial proteins, which form respiratory or oxidative enzymes.
Chloroplast ribosomes (chl. ribosome) –
Chloroplast ribosomes are similar to prokaryotic ribosomes. These have a sedimentation coefficient of 70S and are formed of two subunits, 50S and 30s. The large subunit contains 5S and 23S RNA, and the small subunits have 16S RNA.
These are similar in all groups of plants.
Polysome or polyribosome
During protein synthesis, several ribosomes align with an mRNA molecule. This structure is called a polysome or polyribosome. After synthesizing protein molecules, the ribosome dissociates from the mRNA.
What are the Functions of ribosomes?
Ribosomes are involved in protein synthesis in the cell, but ribosomes alone cannot synthesize proteins. Ribosomes can do protein synthesis only then.
When many ribosomes are arranged in a linear order on the mRNA, this state of the ribosome is called polysome or polyribosome state.
This is the stage when ribosomes take part in protein synthesis. Initially, the subunits of the ribosome are scattered separately in the cytoplasm. These two ribosome subunits are integrated by the magnesium ion Mg2+ as soon as the concentration of Mg2+ reaches 0.001M.
Both the ribosome subunits join together to form a complete ribosome. As this concentration increases 10-fold to 0.01 M, the two ribosomes associate, eventually forming the polysome state.
Friend, if you want information about ribosomes, please share it as much as possible.
Thank you