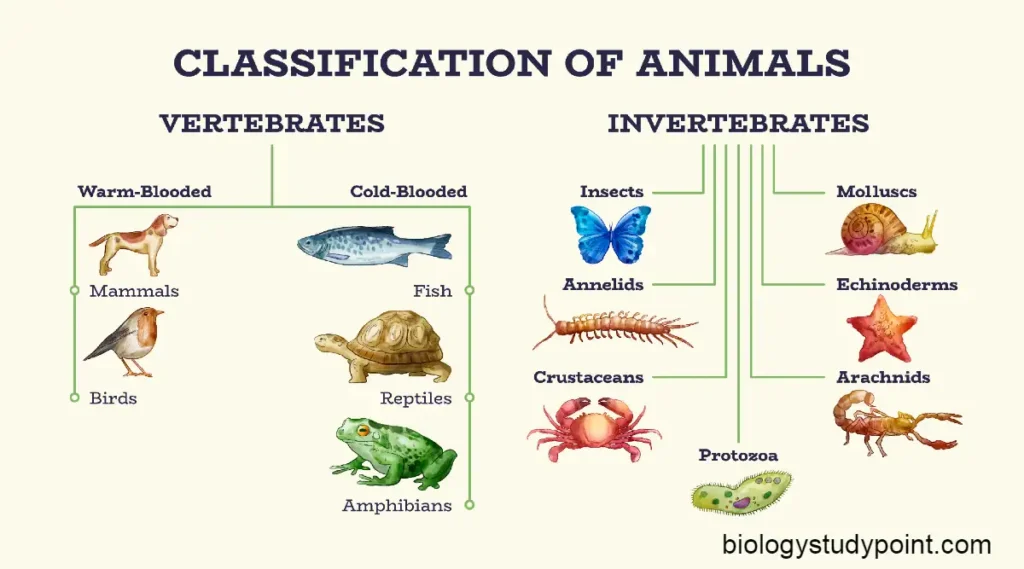
Hello friends, In Today’s article, we will read about the Kingdom fungi in detail and understand them in very simple language. So, let’s start.
What are fungi?
Fungi are a multicellular organism that obtains their nutrition from rotten materials. There are both types of sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction in fungi. Kingdom Fungi are divided into four groups, one of which sexual reproduction is not found, namely Deuteromycetes.
We will read about this kingdom of fungi in detail, so let’s start.
Characteristics of Kingdom Fungi –
- The study of fungi is called Mycology.
- R. H. Whittaker presented the kingdom of fungi.
- Fungi are saprophytic; they get their nutrition from rotten or dead substances. They are also called decomposers because they decompose rotten materials.
- They are cosmopolitan, meaning they are found in all three places: the Hydrosphere, the Lithosphere, and the atmosphere. The living beings who are found in these three circles are called cosmopolitan.
- Their body is multicellular, and eukaryotic cells are found in them. But there is an exception in this KingdomKingdom: yeast is kept, which is single-celled.
- Fungi comprise many cells, each called a hypha. Many hyphae together form a mycelium, the fungi’s body. The word Mycology comes from this Mycelium.
- Fungi filaments are of two types: septate hypha and Coenocytic hypha. When the nucleus of a fungal hyphae divides into two nuclei, a septum is formed between these two nuclei; due to the collapse of the septum, it becomes a bicellular structure, then such a bicellular structure is called septate hypha.
- When the nucleus divides inside the fungal filament to create many nuclei, and the seeds of these nuclei do not form a septum, this multinucleated structure is called a coenocytic hypha.
- The cell wall is made of chitin, which is found in them. Chitin is the second most abundant organic substance on this earth, and the first place is cellulose.
- Both fungi and animals store their food in the form of glycogen.
- When fungi and algae show symbiotic relationships with each other, then that structure is called lichen.
- When some special types of fungi show symbiosis by sticking to the root of some special kind of higher plant, the place where the fungus is attached is called mycorrhiza.
- Fungi reproduce both asexually and sexually.
- There are two types of asexual reproduction: budding and sporulation. There are also two types of spores: conidia and Zoospores.
- In these, a structure is formed for sexual reproduction called a fruiting body. There are many types of spores inside this fruiting body, which act like gametes. The later fusion of these gametes takes place, and after that, a zygote is formed, resulting in a new organism being formed somewhere, and sexual reproduction occurs.
Classification of kingdom fungi
Kingdom fungi are divided into four groups based on sexual reproduction.
- Phycomycetes
- Ascomycetes
- Basidiomycetes
- Deuteromycetes
Phycomycetes
- These are called algal fungi.
- Most of the organisms of this group are found in water, and their structure is like algae. So, they are called algal fungi.
- Their body is layerless; that is, it is multinucleated.
- In this, asexual reproduction occurs, in which spores are formed; now, they can be mobile spores and immobile spores.
- During sexual reproduction, gametes, which are called nymphs, are formed. Both homozygous and heterozygous types of nymphs are found.
- For example, Mucor is called tomato fungus because it infects tomatoes. Rhizopus is called bread fungus because it infects bread.
Ascomycetes
- These are called Sac fungi.
- During sexual reproduction, a fruiting body called an ascocarp is formed. The ascus and its spores are inside this ascocarp.
- These spores act like gametes; that is, they will reproduce sexually. The ascus looks like a space, and this space is called a sac. So they are called Sac fungi.
- These are saprophytic and coprophilous, which means they are found in the feces of animals.
- In these, asexual reproduction takes place by conidia.
- Examples are yeast, Penicillium, and Neurospora. Neurospora is the fungus on which most genetic studies are conducted.
Basidiomycetes
- They are found in the soil and on top of broken tree branches.
- Their fungal net is septate and branched.
- Spores are formed in them for asexual reproduction. Now, they can be mobile spores as well as immobile spores.
- In these, the gametes that will be formed for sexual reproduction are called basidium spores.
- Examples: Agaricus (Mushroom), Puccinia (Wheat Rust), Puffball, and Toadstool.
Deuteromycetes
- There is no sexual reproduction in them.
- Due to a lack of sexual reproduction, they are also called Fungi Imperfect. Imperfect means they do not do all the work, like — do not do sexual reproduction; that is, they are not perfect.
- They reproduce only asexually and produce only immotile spores.
- Their body is striped.
- For example, in an athlete’s foot, this infection is caused by Tinea fungus. An athlete’s foot is called this because this infection is mostly due to sweating in athletes.
You will find the answers to all the questions in the article below.
How do fungi reproduce?
How do fungi obtain nutrients?
What are fungi cell walls made of?
What do fungi eat?
What are examples of fungi?
What are mycorrhizal fungi?
How are fungi classified?
What are the characteristics of fungi?
Friends, I hope you enjoyed the information about fungi. If so, please share it with your friends.
Thanks