Friends, in this article, we will study the Human Health and Disease chapter of the NCERT book. If you wish to read this chapter, then this article is solely for you. We will cover each point of this chapter in this article, so let’s begin without wasting any time.
Human Health and Disease:
Definition of health:
A person who is physically, mentally, and socially healthy is called a healthy person.
Physical health refers to a person being physically strong, and healthy; mental health refers to a person being fit mentally without any mental disturbances, and social health means that the person interacts with people in his/her society, talks, sits, stands, etc.
What is a disease?
When one or more organs, tissues, or systems of the body do not function properly, and various symptoms arise in the body, we call such a person diseased, meaning that the person has a disease.
What is human disease?
Diseases that only affect humans are called human diseases.
How many types of human diseases are there?
There are two types of human diseases:
- Genetic diseases
- Acquired diseases.
What are genetic diseases?
The diseases that we inherit from our parents are called genetic diseases.
What are acquired diseases?
The diseases that we acquire after birth are called acquired diseases. Acquired diseases come in two types:
- Infectious diseases
- Non-infectious diseases.
What are infectious diseases?
The diseases that spread through contact are called infectious diseases, such as the common cold, AIDS, malaria, etc.
What are non-infectious diseases?
The diseases that do not spread through contact are called non-infectious diseases, such as cancer, diabetes, obesity, etc.
Bacterial diseases in humans:
The diseases caused by bacteria are called bacterial diseases. There are many diseases caused by bacteria, but we will only study two bacterial diseases in this study, which are typhoid and pneumonia.
Typhoid:
What causes typhoid?
This disease is caused by a bacterium called Salmonella typhi. This bacterium reaches our small intestine through contaminated food and water, and from there it enters our blood and spreads to other parts of our body, making the person sick.
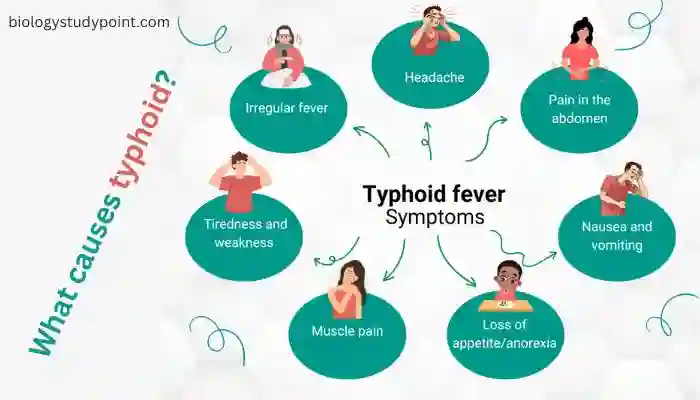
What are the symptoms of typhoid fever?
In this disease, symptoms such as high fever, abdominal pain, constipation, weakness, headache, and loss of appetite occur. In severe cases, there can be a perforation in the intestine, leading to the death of the person.
This disease, i.e., typhoid fever, is diagnosed by the Widal test. There was a woman whose nickname was Typhoid Mary. Let’s find out why. The real name of this woman was Mary Mallon. She was a professional cook and continued to spread typhoid fever for years through the food she prepared. That’s why she was called Typhoid Mary. Although she did not know about this disease, she unknowingly spread it.
what is pneumonia?
Pneumonia occurs due to bacteria called Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae. These bacteria infect the alveoli in our lungs, causing them to fill with fluid and making it difficult to breathe because gas exchange cannot occur.
what are the symptoms of pneumonia?
When a person has this disease, he or she experiences symptoms such as fever, cough, chills, and headaches. But if not shown to the doctor on time, the lips and nails of the person turn blue. This happens because gas exchange cannot occur due to the lack of movement of gases.
Friends, when an infected person sneezes, droplets (droplets of water) come out, and when a healthy person inhales these droplets through breathing or uses the infected person’s utensils, the healthy person also gets infected. Because disease-causing germs are present in those droplets or those utensils, which makes the person infected or sick.
Viral diseases
Diseases caused by viruses are called viral diseases. Here, we will study only one viral disease.
What is the common cold?
It is also called rhinitis. The rhinovirus causes this disease. This virus infects our nasal passages, meaning the nose and respiratory tract, but it does not infect our lungs.

What happens is that this virus forms a layer in our nose called the Schneiderian membrane, or olfactory membrane. It infects this layer, reducing our sense of smell and causing excessive production of mucus inside us so that other rhinoviruses cannot enter us.
This disease is transmitted when droplets expelled by an infected person through sneezing or coughing enter the respiratory system of a healthy person or when a healthy person uses an object used by an infected person.
Symptoms of the common cold:
- The nose gets blocked because excessive mucus fills it.
- A hoarse voice occurs because this virus also infects our throat or pharynx.
- Coughing occurs, accompanied by headaches, fatigue, and other problems.
- This illness lasts for three to seven days.
What are protozoan diseases?
Diseases caused by protozoan parasites are called protozoan-borne diseases. Here, we will study the diseases caused by protozoan parasites.
Malaria:
How is malaria transmitted?
This disease is caused by a protozoan parasite called Plasmodium, which is a single-celled and obligate parasite. Plasmodium has several species, but we will talk about four important species.
- Plasmodium falciparum:
This species is the most dangerous, meaning it is fatal, and it is found second in number in India. It causes malignant tertian malaria. Malignant means severe/deadly, tertian means 3, and three means fever occurs on the third day, meaning every 48 hours, and malaria is a common term.
- Plasmodium vivax:
This species is slightly less dangerous than the first one, meaning it is not fatal. It is found in the highest number in India. It causes Benign Tertian malaria. Benign means mild, meaning it is not fatal, tertian means 3, and three means fever occurs on the third day, meaning every 48 hours, and malaria is a common term.
- Plasmodium malariae:
This species is a bit less dangerous. It is found third in number in India. It causes Benign Quartan Malaria. Benign means mild, meaning it is not fatal, quartan means 4, and four means fever occurs on the fourth day, meaning every 72 hours, and malaria is a common term.
- Plasmodium ovale:
This species is the least dangerous. It is hardly found in India. It causes Benign Tertian malaria. Benign means mild, meaning it is not fatal, tertian means 3, and three means fever occurs on the third day, meaning every 48 hours, and malaria is a common term.
The lifespan of Plasmodium:
Plasmodium is digenetic, meaning organisms that spend their life cycle in two different hosts or environments are called digenetic. Its primary host is the female Anopheles mosquito, and the secondary host is a human. Now you might wonder why the female Anopheles mosquito is called the primary host and why the human is called the secondary host. In the secondary, you only mentioned humans without specifying male or female. So let me answer that question too.
See, organisms that complete their life cycle in two different hosts and reproduce sexually in one host are called primary hosts. We have seen that the sexual reproduction of Plasmodium occurs inside the female Anopheles mosquito, so the female Anopheles mosquito is called the primary host. Plasmodium is the best vector for female Anopheles mosquitoes.
Because the nourishment of the female Anopheles mosquito comes from our blood, and it sucks our blood. Plasmodium enters humans through our blood when the female Anopheles mosquito bites, whereas the nourishment of the male mosquito comes from nectar, not from piercing. But the female mosquito also pierces, so it easily pierces and sucks the blood.
After entering humans, Plasmodium demonstrates sexual reproduction, so it is called the secondary host in humans. Whether male or female in humans, both can complete their life cycle within either.
Plasmodium Life Cycle:
Plasmodium is found in the saliva of the female Anopheles mosquito and is in a state called sporozoite. This stage is called the infective stage because, when a female Anopheles mosquito bites us, it enters our blood. Once a mosquito bites, 5 to 10,000 Plasmodium enter our blood. After reaching the blood, they need nourishment, and for nourishment, they require glycogen and globin protein.
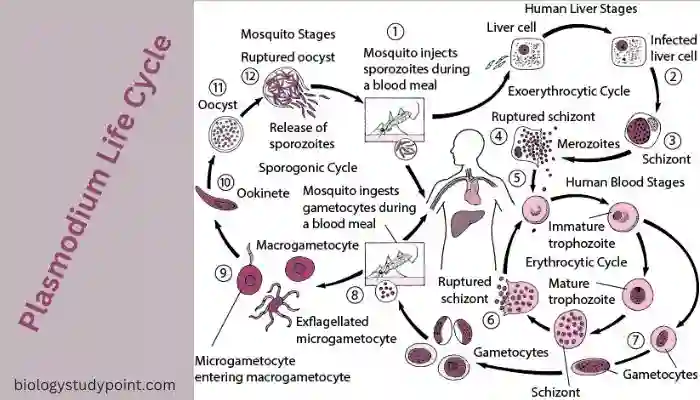
First, they flow into the liver in our blood for glycogen because glycogen is abundant there. When these Plasmodium or sporozoites reach the liver, this state of Plasmodium is called Schizont. Now these schizonts will consume or eat the glycogen present in the liver, and after eating, they will receive energy, and using this energy, these schizonts will break themselves into small pieces.
These small structures are called merozoites. This process of division is called multiple fission, and multiple fission is a type of asexual reproduction. This multiple fission is called schizogony. All these activities are happening inside the liver, and the merozoites are inside the liver cells. After breaking these cells, merozoites return to the blood.
Now they need nourishment; they need globin protein for nourishment. Where will they find globin protein? Let’s find out. Friends, globin protein is found in our blood itself. As you know, in the blood, there are RBC cells, and inside these RBC cells, there is a pigment called hemoglobin. This hemoglobin has four parts, in which 2 alpha and 2 beta polypeptide chains are found. When these two combine, they are called globin proteins. Iron (Fe+2) is also found in it, and this iron gives hemoglobin a red color, 80% of RBCs are found in our blood cells, which is why our blood is red.
The job of RBCs in our blood is to carry oxygen, and hemoglobin in RBCs carries oxygen. Each part of hemoglobin, which is made up of four parts, binds one oxygen atom from each part, meaning one hemoglobin carries four oxygen atoms.
Now you must be wondering why I told you all this because merozoites have come into our blood, and what nourishment do they need? Globin protein, which is present in RBCs, These merozoites go into the RBCs. From there, they consume the globin protein, which gives them energy, and they start growing. And when they grow, they break themselves into smaller pieces, and the structures they create are called cryptomerozoites.
Now, iron (Fe+2) will remain in the RBCs. These cryptomerozoites extract this iron and break it into smaller pieces. These pieces of iron are called Haemozoin. Now in one RBC, filled with cryptomerozoites and small pieces of iron, the RBC bursts, and from bursting, cryptomerozoites and haemozoin enter the blood. These haemozoin keep flowing with our blood and will collide with muscles and stimulate muscles for irregular contraction and relaxation, causing our muscles to contract and expand, making us feel shivering.
Now, these cryptomerozoites that have come into our blood will leave the RBCs and go back inside, and when they go inside, we call this stage Trophozoite. Now these Trophozoites will consume the globin protein, and using that energy, they will divide themselves and create structures called gametes. Now many gametes will fill inside the RBCs, which will cause the RBC to burst and the gametes to enter the blood.
Now, when a female Anopheles mosquito bites an infected person and sucks blood, these gametes will move into the mosquito’s stomach and fertilize there because there are favorable conditions for fertilization, and as a result of fertilization, zygotes are formed, and this zygote is called an ookinete.
Fertilization and the formation of zygotes are sexual reproduction processes. To prevent the zygotes from breaking in unfavorable conditions, they build a wall around themselves, called a cyst. This entire structure is called an oocyst. In which there is a cyst from the outside and a zygote inside, called an ookinete.
Now this ookinete or zygote will again undergo multiple fissions and break into small structures inside the cyst, and these small structures are called sporozoites. The process of multiple fissions that have occurred is called sporogony. Finally, these sporozoites, coming from the mosquito’s gut, reach the salivary gland of the mosquito, and ultimately, when the female Anopheles mosquito bites again, they enter the human again. This is how its life cycle continues.
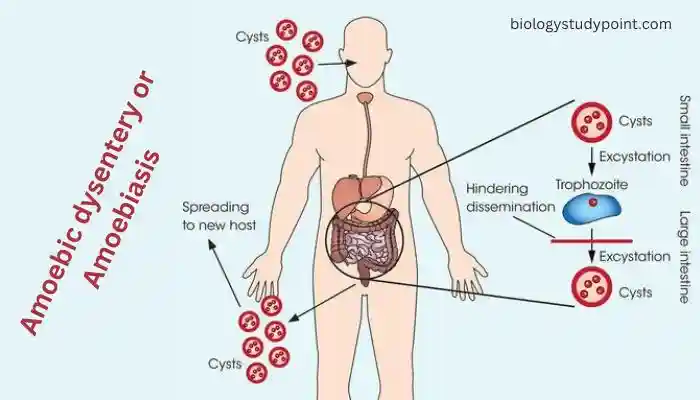
Amoebic dysentery or amoebiasis:
This disease is caused by a protozoan organism called Entamoeba histolytica. This protozoan is mostly found in contaminated food and feces. When flies sit on contaminated food or feces, they get stuck to their legs. Then, when these flies sit on our food, Entamoeba histolytica is deposited on it, and when we consume that food, it enters our body and makes us sick.
Amoebiasis symptoms:
- This causes pain, cramping, constipation, and bloody stool in our stomach.
Worm Diseases:
Those diseases caused by worms are called worm-related diseases. We will study two worm-related diseases.
What is ascariasis disease?
This disease is caused by a worm called Ascaris lumbricoides. This worm enters our body through contaminated water, vegetables, fruits, etc., and causes infection. The eggs of these worms are found in water. This disease leads to fever, muscle pain, anemia, internal bleeding, intestinal blockage, etc. Mainly, they affect our digestive tract.
Filariasis or elephantiasis:
This disease is caused by two worms, Wuchereria bancrofti and Wuchereria malayi. This disease is caused by the bite of a female Culex mosquito. When this mosquito bites, these insects enter our body and infect the lymphatic vessels of our legs, due to which they swell and our legs become thick. Additionally, it infects the scrotum in men, causing swelling there too.

Fungal Diseases:
Diseases caused by fungi are called fungal diseases.
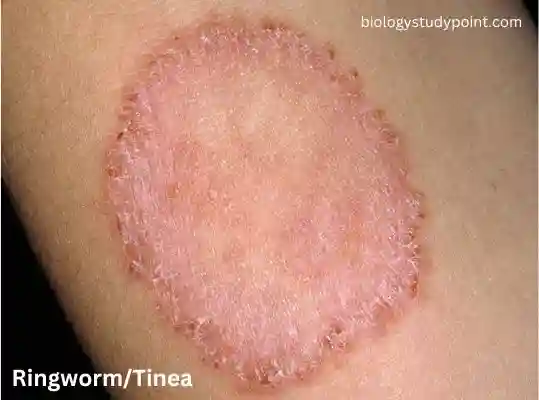
What is a ringworm?
There are mainly three genera of fungi responsible for ringworm, or tinea. Microsporum, epidermophyton, and trichophyton This disease mainly affects the skin, hair, and nails.
Disease Control:
To control these diseases, you need to do some things like keep yourself clean, drink clean water, and maintain cleanliness around you. Places like mud, drains, and potholes, where water stagnates, need to be kept clean. Using mosquito nets while sleeping. You can also put gambusia and guppies, fish that eat mosquito larvae, in places that are stagnant water bodies. You can use pesticides to kill pathogens.
Human Immune System Read more >>