Hello friends, do you want to know about Kingdom Protista? If yes, then you have come to the right post. Today, we will explain Kingdom Protista to you step by step. Let’s start.
What is Kingdom Protista?
In this Kingdom, single-celled organisms with eukaryotic cells have been placed. Only a few of them have a cell wall containing a nuclear membrane. Their nutrition mode is mixed, meaning they are both autotrophs and heterotrophs. Their method of reproduction is gamete-conjugation and conjugation.
Characteristics of Protista
- Eukaryote organisms are kept in this Kingdom. This means that eukaryotic cells are found. And those cells in which a concentrated nucleus or nuclear envelope is found are called eukaryotic cells.
- Single-celled organisms are kept in this Kingdom.
- Most of the creatures in this Kingdom are aquatic and, in this type of water, are found in salty water.
- The organisms of the Protista kingdom are both autotrophic and heterotrophic. They also contain mixed nutrients, which means that when autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition are present inside the same organism, they are called mixed nutrients.
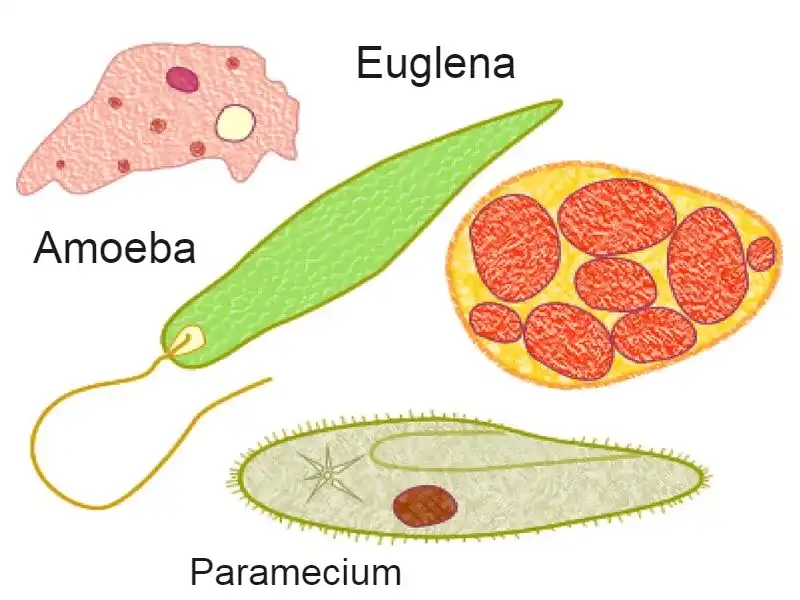
- Example – Euglena It has both types of nutrition.
Classification of Kingdom Protista
The Kingdom Protista is divided into three parts based on nutrition.
- Autotrophic/Photosynthetic Protist
- Consumer protists
- Consumer (Parasitic) protist
Autotrophic/Photosynthetic –
Organisms that make their food and are not dependent on other organisms are called autotrophs. They are placed in three types of groups.
- Chrysophyte
- Dinoflagellate
- Euglenoid
Consumer (Symbiotic) –
The organisms that depend on others for nutrition or food are called consumers. Meaning of saprophytes: The microorganisms that get nutrition from rotten or dead substances are called saprophytes. There are bacteria and fungi. Similarly, there is an organism in the Kingdom Protista called slime mold. So, the downy mildew is kept in this group.
Consumer (Parasite) –
Protozoa have been kept in this group, and parasites, organisms that depend on other organisms for nutrition and accommodation, are called parasites.
Examples are lice, Ticks, etc.
Chrysophyte –
- Two types of creatures have been kept inside it. Diatoms and Desmid (Golden Algae): This paper will mainly study diatoms.
- They are found in fresh water and marine water mostly found in marine water.
- These are Phytoplankton, which means they are autotrophic and float on the water’s surface.
- Chrysophytes make the maximum food on this earth, and in this, chrysophytes also make maximum diatoms. Hence, they are also called main producers because they do maximum photosynthesis on this earth.
What are diatoms?
- Their cell wall becomes hard when they absorb the silica present in water. This rigid cell wall is called a frustule. This frustule is made of two parts. The first upper part is epitheca, and the second lower part is hypotheca.
- Why are they called diatoms? See, the meaning of Di is two, and here, the meaning of atom is covering; now, these two coverings are made up of epitheca and hypotheca. Hence, they are called diatoms, and their structure is like a soap dish.
- When these Diatoms are dead, they get collected at the base of the sea. They were not affected by acid, high temperature, or light because their cell wall was hard. Now, this gathering structure is called Diatomy Soil or Diatomite.
Use of diatomic soil –
- It is used in making paint.
- Used in making toothpaste.
- Used in making wood polish.
- Used in making oil.
- It is used in making walls of furnaces because they are not affected by high temperatures.
- These diatoms act as pollution indicators. Pollutant indicator means that water which has pollutant elements in it, then these diatoms will not grow there.
What is polluted water?
The water in which the dissolved oxygen is less is called polluted water. Now, in the water where the amount of oxygen is low, organisms will not be able to survive, and if diatoms are put in such water, they will also not survive. We get information from them that this water is polluted. Hence, they are called pollutant indicators.
Examples – Triceratum, Navicula, Cymbella, etc.
Now, friends, we will read about Dinoflagellates.
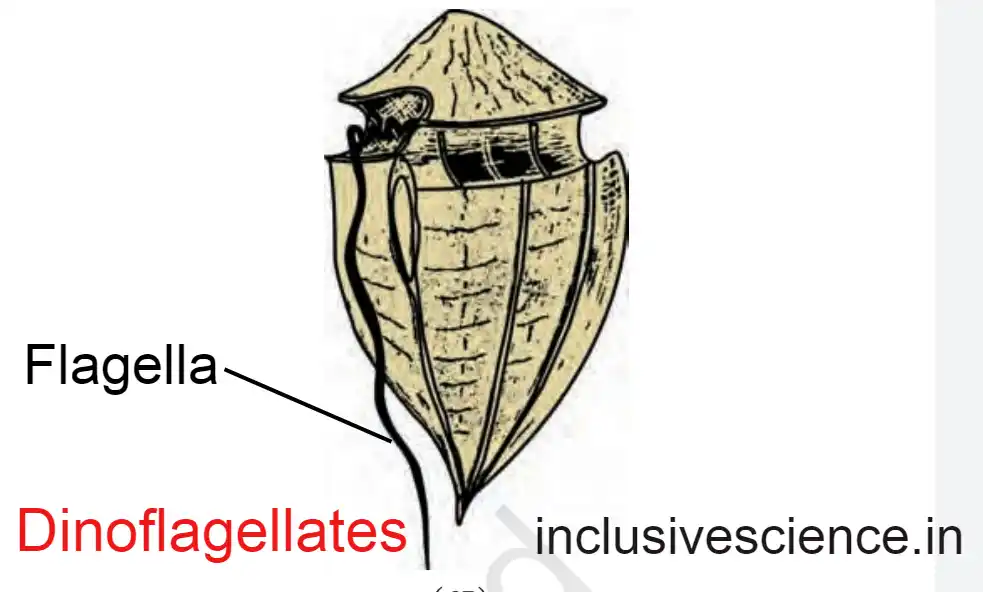
What are dinoflagellates?
- These are green, yellow, red, brown, and blue; they will be the same color as the pigment inside them. If there is a red pigment, it will be red; if it is yellow, it will be yellow.
- These are mostly found in saline water or the sea.
- Their cell wall is made of cellulose and pectin, so the cell wall becomes very rigid. This hard cell wall is called Lorica; it works as a shield or weapon.
- Their bicellular structure means two flagella are found in them, which is why they are called Dinoflagellates. Dino means two, and Flagellate means flagellum.
One flagellum is perpendicular to the body, called the sulcus, and one is found transverse to the body, called the annulus.
Note1 – Some dinoflagellates show bioluminescence, which means they make light in the dark of night. E.g. Noctileuca, Pyrodinium.
2 – Due to some dinosaur fossils, red waves come from the sea, which is called red tide. Like – Gonialax, Gymnodinium, etc.
Now, friends, we will read about Euglenoid, so let’s know it too.
What are euglenoids?
- They are mostly found in clear water.
- The cell wall is not found in these, but in its place, a flexible, protein-rich membrane is found, which is called a Pellicle.
- There is an involution in their front; it is folded inwards. Two flagella emerge from inside this involution; one is long, and the other is short. Euglena moves rapidly with this long flagella.
- A structure is found near the base from where the flagellum emerges, which is called the photosensitive eye spot or Stigma; its function is to move the euglena toward the light.
- A contractile vacuole is found inside them, whose work is to control the amount of water; that is, if the amount of water inside them increases, then it expels the water, and if it decreases, then the water is released. Accumulates.
- Euglena contains photosynthetic pigments such as chlorophyll-a, chlorophyll-b, and xanthophyll found in higher plants.
- They store their food in the form of paramylon starch after photosynthesis.
- Its nutrition is mixed, which means it makes its food by photosynthesis during the day, while it eats Diatom/Dinoflagellates the night, which means it is both autotrophic and heterotrophic, and in both these types of nutrition are available; they are called mixed nutrition.
What are Slime Moulds?
- These are saprophytes.
- It is mostly found in yellow color.
- They are single-celled.
- The cell wall is not found in them.
- They contain naked protoplasm. Which is multicentric, and its name is Plasmodium.
- Under favourable conditions, these Slime moulds come close together and form a colony. Favorable conditions mean they are getting enough food and water.
- In unfavourable conditions, these Slime moulds live far away from each other. In this condition, they shrink their protoplasm and form a structure called a fruiting body. All cell organelles are present in this protoplasm.
- I have already told you that there are many nuclei in these, and around each of these nuclei, the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi body form the cell membrane. After that, they create another covering over the cell membrane called the cell wall.
- Now, each nucleus has changed into a new structure called Spore. We can also call this Spore a new cell. Now, many spores will be formed inside the fruit body, so the membrane of the fruit body will burst, and all the spores will come out.
- Now, in what condition have these spores come out? In unfavourable conditions, will these spores die? Will they not die because these spores are surrounded by a strong cell wall that protects them as soon as this favourable condition? When they come in, their cell wall breaks down, and they start nourishing.
- After that, there is a division of the nucleus in their cytoplasm, which causes many nuclei to form in them, and as a result, they become multinucleated. That is, they turn into Plasmodium like before.
What are protozoa?
Scientist Anton van Leeuwenhoek first discovered protozoa.
These are parasites or can be predators. Predators are those organisms that eat or get nutrition by killing other microorganisms. They are called predators.
Classification of Protozoa
Protozoa are classified based on locomotor organs. This means the part by which the living beings move.
Protozoa are divided into four parts.
- Amoeboid protozoans
- flagellated protozoans
- Ciliated protozoans
- Sporozoans
Amoeboid protozoans –
- You must have come to know from the name which creature has been kept in it. Amoeba is placed.
- The organ that helps in walking is called pseudopodia. False feet mean whose shape keeps changing, and what is termed feet – The structure that comes out of the body is called feet.
- Like our hands and feet, in the language of science, they are called forefeet and hind feet. Now the shape of our hands and feet does not change, but when amoeba has to move, the shape of the fart that comes out of them keeps on changing; that is why their locomotion organ is called pseudopod.
- Their locomotor organs help not only in walking but also in catching food.
- Amoeba is found in both fresh and marine water. They are also found in wet soil.
- Examples – Amoeba proteus and Entamoeba histolytica. Amoeba proteus is found in seawater, and Entamoeba histolytica is found in freshwater, which causes amoebic dysentery in humans.
Flagellated protozoans –
- In the organisms of this group, the movement organ is the flagellum.
- Most of the organisms in this group cause diseases.
- Example – Trypanosoma gambiense. This is a parasite found in the saliva of the Tsetse fly. Its scientific name is Phlebotomus argentipes, and when this fly bites a person, Trypanosoma gambiense enters that person and causes a disease called sleeping sickness.
- In this disease, the person is not able to sleep properly. There is restlessness, no time left to sleep, and his entire sleeping time gets spoiled.
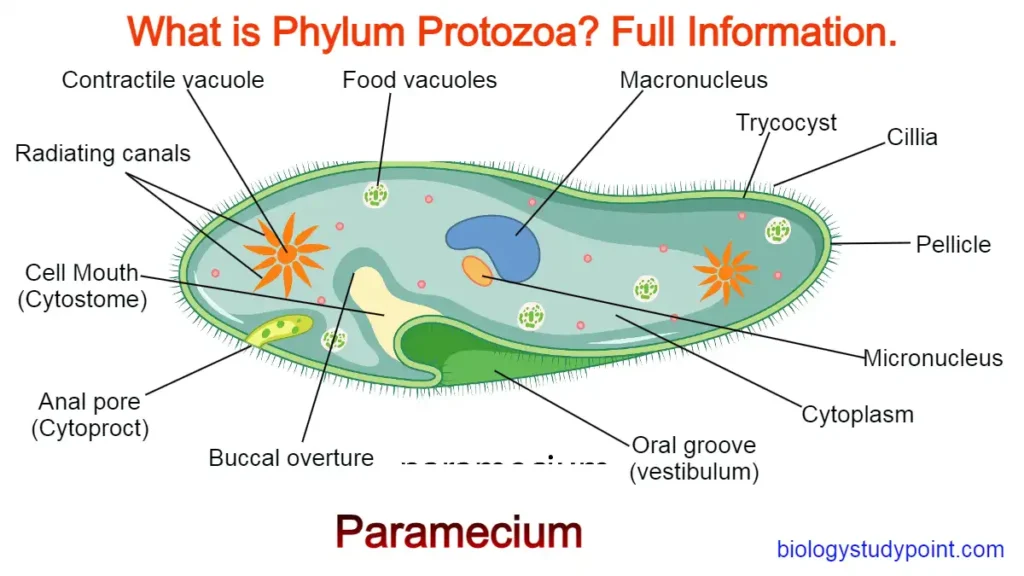
Ciliated Protozoa –
- It has locomotor organs (cilia). Along with moving from the organism, these cilia also make the substances present in the environment, like food.
- Example – Paramecium codetum, which feeds on Phytoplankton and zooplankton. That means it is a predator.
- It is binucleated. There is a small nucleus called the short nucleus, which undergoes mitosis, and a large nucleus called the long nucleus. It does asymmetric division.
Sporozoans –
- They do not have locomotor organs.
- They travel through carriers. The carrier can be water, air, or even an animal. For example, Plasmodium organisms are transmitted by female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- Most Sporozoa are parasitic.
- Example – Levrane discovered Plasmodium, which causes malaria, which is transmitted through the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito. Sir Ronald Ross reported that Plasmodium is present in the saliva of female anopheles.
There are mainly four species of Plasmodium.
- Plasmodium vivex
- Plasmodium falciparum
- Plasmodium malariae
- Plasmodium ovale
Some important questions and answers.
Q.1 Which organisms come in Protista?
Ans. Eukaryotic cells are single-celled organisms.
Q.2 Where do protists usually live?
Ans. Lives in water.
Q.3 The link between the two animal groups of Protista is?
Ans. Euglena
Q.4 Into how many parts is the Protista kingdom divided?
Ans. The Kingdom Protista is divided into three parts based on nutrition.
- Autotrophic/photosynthetic protist
- Consumer protists
- Consumer (parasitic) protist
I hope you, friends, liked the information given about the Kingdom Protista. If you like it, share it on your social platform.
Thank you