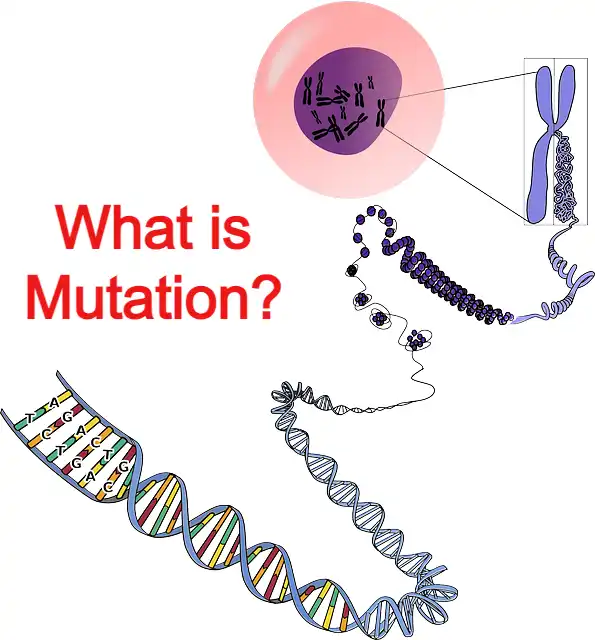
Hello friends, Today we will study a very important topic, namely, what mutation is. Friend, you must have seen one or the other movie with mutation. Friends, we will study mutation thoroughly step by step, so let’s start.
What is mutation?
Definition of Mutation –
A sudden change in the genotype and phenotype of an organism is called a mutation.
Changes in the DNA/nucleotide sequence of the somatic cell and the gamete cell. It is called a mutation.
What is Variation?
When mutation and recombination occur together, a new species is formed, which is called speciation. When this action forms a new form of the organism, it is called transformation.
How many types of mutations?
There are three types of mutations.
- Genetic Mutation
- Gene Mutation
- Chromosomal Aberrations
What is Genetic Mutation?
When there is a change in the number of chromosomes of an organism, it is called a genetic mutation.
It is of two types.
- Aneuploidy
- Euploidy/Polyploidy
Aneuploidy –
There is a change in the number of chromosomes if chromosome segregation or segregation fails during cell division.
Euploidy/Polyploidy –
It is commonly found in plants. In this, there is a change in the entire set or collection of chromosomes if cytokinesis (a division of the cytoplasm) fails after telophase.
What is Gene Mutation?
Any change in the structure, configuration, or number of genes is called gene mutation. A gene mutation can be of two types.
- Frameshift
- Replacement
Frameshift –
Such a change in the structure of a gene, due to which its entire gene structure changes, is called a frameshift mutation.
It is of the following three types.
- Deletion
- Addition
- Substitution
Deletion –
In this, the change in gene structure is due to the decrease in nucleotides.
Addition –
In this, the change in gene structure is due to the increase in the number of nuclease tides.
Substitution –
The number of genes remains unaffected, and the nucleotide is exchanged.
It is of the following two types.
- Transition
- Transversion
Transition –
In this, the exchange takes place between similar nuclei.
For example, purine is exchanged with purine and pyrimidine with a pyrimidine.
Transversion –
In this, the exchange occurs between unequal nuclei; that is, the exchange of purine with pyrimidine and its substitution mutation can be of the following three types in addition to the above.
1- Silent Mutation –
The codon is changed in this, but the codon codes for the same amino acid.
- Missense Mutation –
The codon is changed to change the codon codes for a different amino acid.
- Nonsense Mutation –
In this, the normal codon is converted into a nonsense codon.
Chromosomal Aberrations
When there is a change in an organism’s chromosome structure, it is called a Chromosomal Aberration, in which two changes are involved.
Out of this, there is a change in the arrangement of genes present in the first chromosome, or there is a change in its number. It is also called Structural Aberrations.
It mainly occurs during the reduction division.
Due to chromosomal abnormality
The chromosomal abnormality is caused by the breakage of the chromosome and the rejoining of the broken fragment in the abnormality. Chromosome breakage can be induced by radiation (X-rays, gamma rays), chemical mutagenic agents such as insecticides, herbicides, alkali analogs, and viruses. Chromosome breaks are also induced in some genes.
Structural Changes in Chromosomes
It is of two types.
- Change in The Number of Genes
- Change in the Arrangement of Genes
Change in the Number of Genes
In this, there are changes in the number of genes.
Deletion – In this, one or more genes decrease due to the breakage of chromosomes, and only the broken part decreases.
Duplication – It is the addition of one or more genes, as a result of which the organism bears duplicated genes in its haploid chromosome complement.
Change in the Arrangement of Genes
In this, there is a change in the systematic form of the gene.
Translocation is the exchange of parts between non-homologous chromosomes to form new chromosomes.
Inversion – This involves the rotation of a block of genes within a chromosome by 180 degrees.
Friends hope what mutation is. You must have liked the information about (What is Mutation in Hindi?). Friends, if you like this information, please share it as much as possible.
Thank you

I need to to thank you for this good read!! I certainly loved every bit of it. I have you bookmarked to check out new stuff you postÖ