Hello, guys. In today’s article, we will study Multiple alleles. Like – Multiple Alleles’ Definition of Biology? Characteristics of multiple alleles. We will know the answers to many such questions today, so let’s start.
Multiple alleles’ definition of biology
These are members of the same gene pair located on the same locus, and all control the same character, but each allele affects it somewhat differently.
What are multiple alleles?
Observing the segregation and recombination of bodily characters infers the existence of genes. Only genes that give rise to at least two distinguishable alleles are known.
Mendel dealt only with a pair of alleles, i.e., one standard and the other mutant. However, the normal gene can mutate in more than one way, giving rise to several alternative states. Cases are known where sets of alleles contain three, four, or even more members. Such sets are known as multiple alleles.
Characteristics of multiple alleles.
- Multiple alleles arise through mutations of the same gene at different times and to a different extent.
- Multiple alleles occupy the same locus within the chromosomes.
- As there are only two chromosomes of each kind in a cell, there are only two genes of a series at a given locus in a diploid cell but only one in the gamete.
- Multiple alleles affect the same trait, but each has a different manifestation. Sturtevant had described them as carrying the same function but with varying efficiency. These act in some way to control the various steps in a chemical reaction.
Differences Between Multiple Alleles and Multiple Factors –
Multiple alleles differ from the various factors because the numerous alleles refer to genes at a given locus. In contrast, the various factors refer to genes at other loci that interact to produce a specific trait.
1. Multiple Alleles in Rabbit –
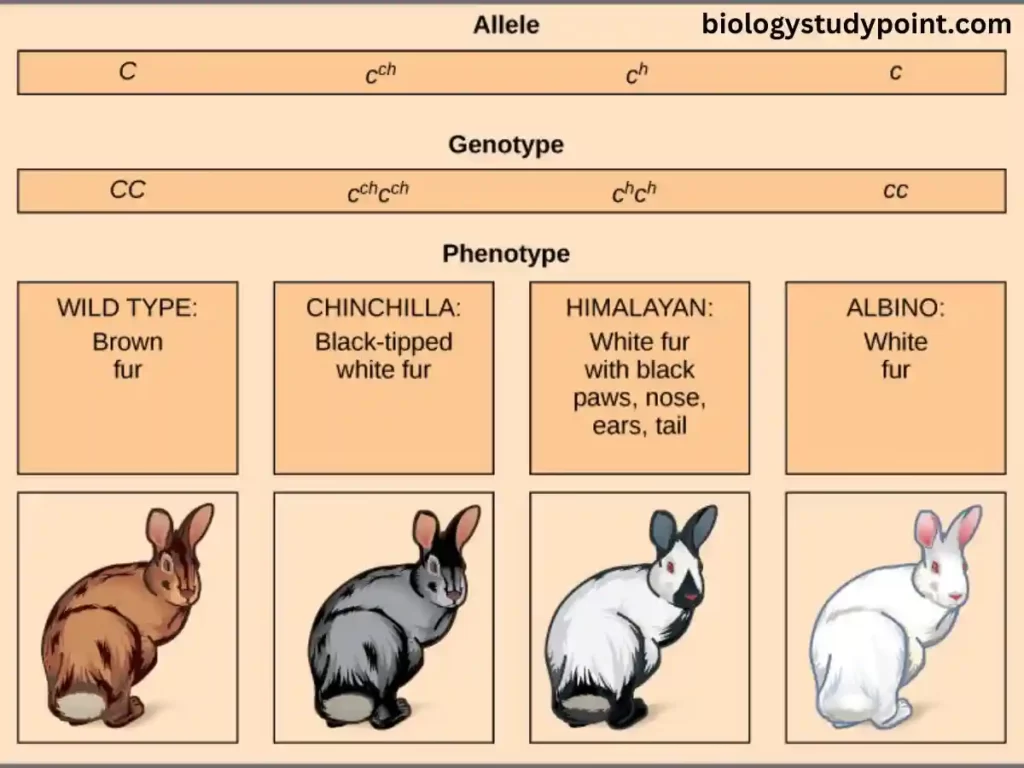
In rabbits, the coat color genes of the multiple series are related to each other as follows :
The C or full color is dominant over other alternatives. Chinchilla (C ch) is recessive to full color but dominant to others (Himalayan and albino). Himalayan (Ch) is recessive to Chinchilla and full color but is dominant over albino. Any of these allelomorphic pairs, if homozygous, will breed true, and if heterozygous, will result in the familiar 3 1 ratio.
| S. No. | Genotype | Phenotype | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | CC or ++ | Full color or Agouti | Dark brown and uniform color |
| 2. | Cch Cch (i) Cch1 (ii) Cch2 (iii) Cch3 | Chinchilla | Silvery gray, uniform color Dark Chinchilla Intermediate Light gray |
| 3. | Ch | Himalayan | White fur, pink eyes but feet, nose, ears and tail are brown or black. |
| 4. | c | Albino | No pigment |
Segregation and Recombination of Multiple Alleles –
As we know, a normal gamete carries only one member out of the multiple series, so the union of two brings the two genes of an allelic series together. The two memes may be in any possible combination.
Whenever the two members of an allelic series are crossed, it is found that their F2 generation always contains homozygous dominant, heterozygous, and homozygous recessive in the ratio of 1: 2: 1, for example :
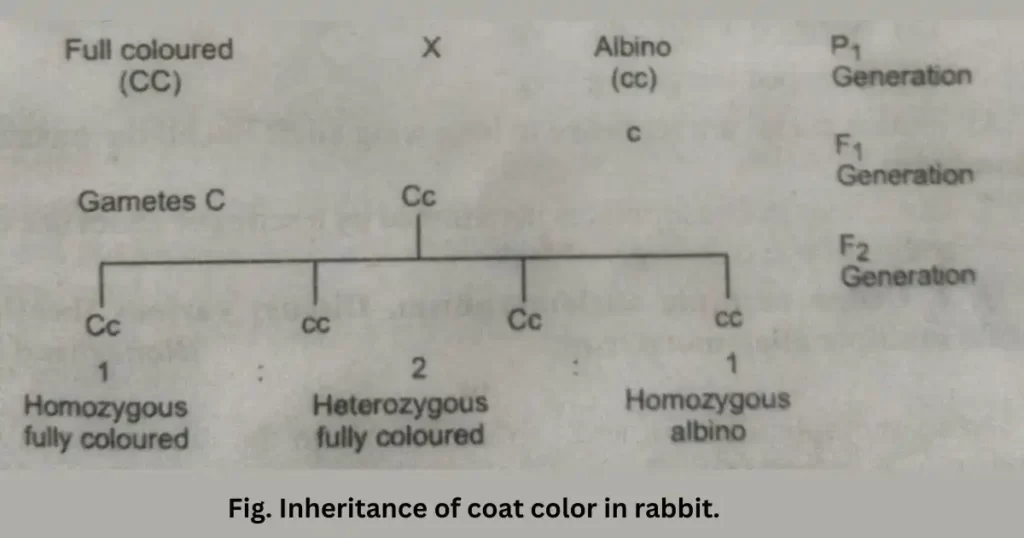
A cross between a fully colored rabbit and an albino rabbit results in 1CC: 2Cc: 1 cc in F2 generation. These genes in rabbits are related as dominant and recessive; hence, colored and albino rabbits are produced in a ratio of 31.
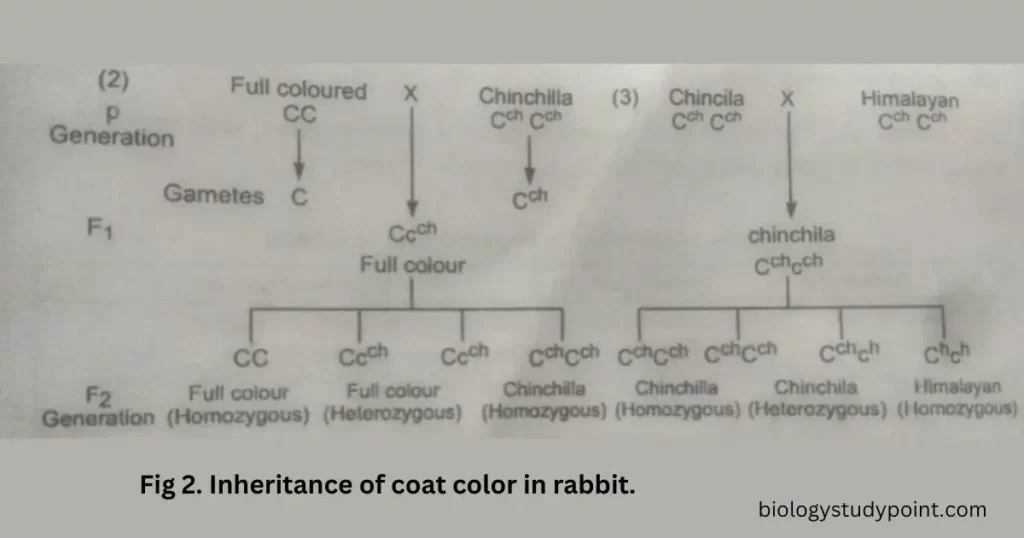
The principle underlying the segregation and recombination applies to crosses between any other two genes of that series, e.g., If Chinchilla and albino are crossed, they will produce Chinchilla (Homo), Chinchilla (hetero) and albino in a 1: 2: 1 ratio.
The appearance of F1 and F2 individuals will depend upon the degree of dominance of the genes involved. The alleles are not always related to dominant and recessive; sometimes, they blend.
2. Multiple Allelic Series in Drosophila –
In Drosophila Melanogaster, a number of multiple alleles are known.
1. Wing character
- Long wings : ++ or Vg+ Vg+ (wild type)
- Vestigial wings : vg vg
- Antlered wings : vga vga
- Nicked wings: vg ni vg ni
- Notched wings: vg no vg no
- Strapped wings: vg st vg st
All mutant alleles are recessive to long-wing alleles, but all the mutants are codominant.
2. Eye color in Drosophila is determined by a series of about one dozen black alleles of the eye color gene.
Define multiple allomorphism. Discuss various theories to explain multiple allelomorphism.
- Theories of Multiple Allelomorphism -Theory of point mutation – It Means that a given gene at a given locus mutates, producing different effects.
- Close linkage of pseudoallelism – Drosophila has a standard red eye color. Mutation Occurred from red to white and to various other light shades of red. Recently, Lewis found that flies hybrid for apricot and white produce red offspring when crossing over is significantly increased—these red hybrids are always crossovers. Lewis concluded that apricot and white are not alleles but occupy adjacent loci and are pseudo alleles.
- Heterochromatin theory of allelism – Chromosomal breakage and rearrangement sometimes bring the heterochromatin next to genes, suppressing the expression of genes in question. In maize, there is evidence that position effects are sometimes due to the transposition of very minute fragments of heterochromatin that are too small to be visible under a microscope.
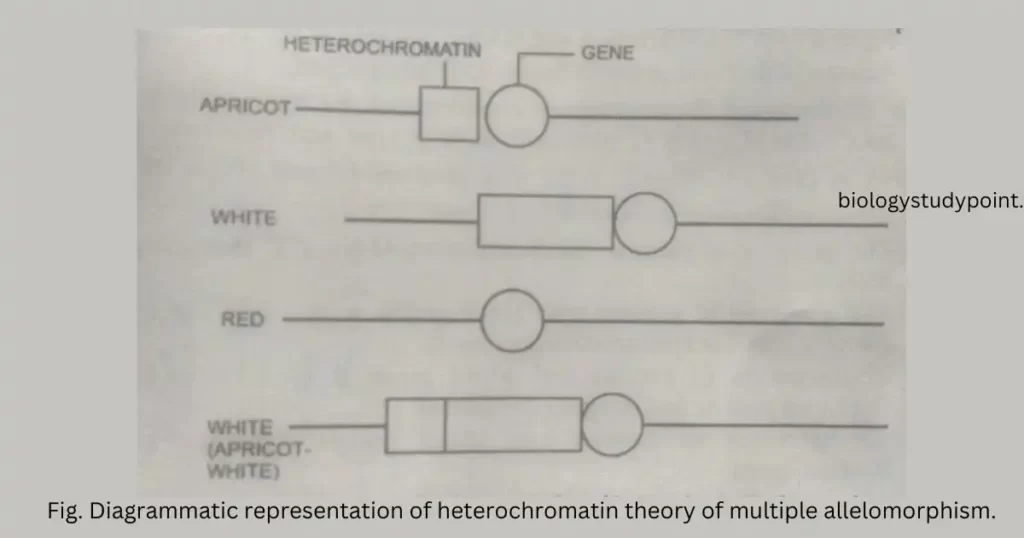
It is often difficult to tell which theories explain a particular allelism case; all three may apply in different cases.
4. Suballeles and iso-alleles – In maize, the ‘R‘ series for the purple aleurone and purple plant color behave like a compound gene. Stander has found that these genes from different strains are not precisely alike because they result in different pigment distributions. These alleles are known as suballeles.
Alleles that produce the same phenotypic effect in homozygous conditions but differ are called iso-alleles. In Drosophila, whites of different origins are not alike. For, when separate strains of whites are crossed to flies that carry one of the intermediate alleles (as eosin), the hybrids are not alike; some might show more dilution of eosin than others.
Define multiple allelism and explain its role in the inheritance of the ABO blood group in man.
Blood Groups in Man –
Human blood groups are an example of multiple alleles. The human population has 4 blood groups: A, B, AB, and O. These are determined by the presence of a specific mucopolysaccharide, the carbohydrate groups bound to lipid molecules of the membrane of red blood corpuscles. This substance is called an antigen.
- Persons with blood group A have antigen A
- Persons with blood group B have antigen B
- Persons with blood groups A and B have antigens A and B
- Persons with blood group O do not have any antigens.
The synthesis of these antigens is controlled by three alleles – IA, IB, and IO. Blood group O phenotype is wild type and recessive. Gene IO IO controls it. Thus, IO is the wild gene, and LA and LB are its two mutant alleles that exhibit codominance. Thus –
- The genotype of persons with blood group O is – IO IO (homozygous recessive).
- The Genotype of persons with blood group A is – LA IO or LA LA (heterozygous or homozygous dominant).
- The genotype of persons with blood group B is – LB IO or LB LB (heterozygous or homozygous dominant).
- The genotype of persons with blood group AB is – LA LB (Dominant).
The genes A and B are dominant to gene IO but are codominant to each other, and both are expressed when present together.
| Blood Group | Genotype | Antigen Present | Nature |
| O | Io Io | None | Recessive |
| A | LA LA or LB IO | A | Dominant |
| B | LA LA or LB IO | B | Dominant |
| AB | LB LB | AB | Codominant |
Inheritance of blood group –
The genes A and B are dominant over gene IO but are codominant to each other, and both are expressed when present together.
If a person homozygous for blood group A marries a woman with blood group O or vice versa, all her children will have blood group A.
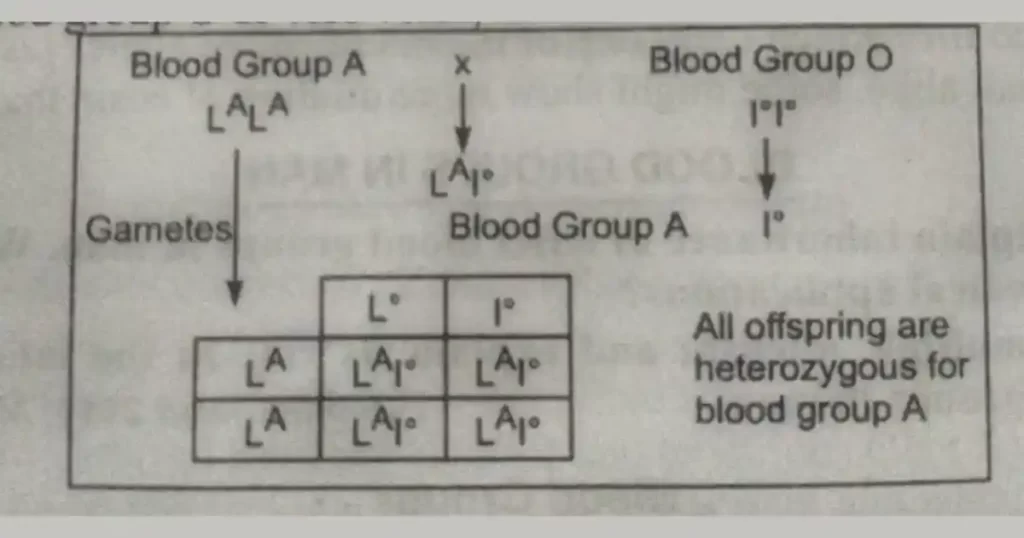
If a person homozygous for blood group B marries a woman with blood group O or vice versa, all her children will have blood group B.
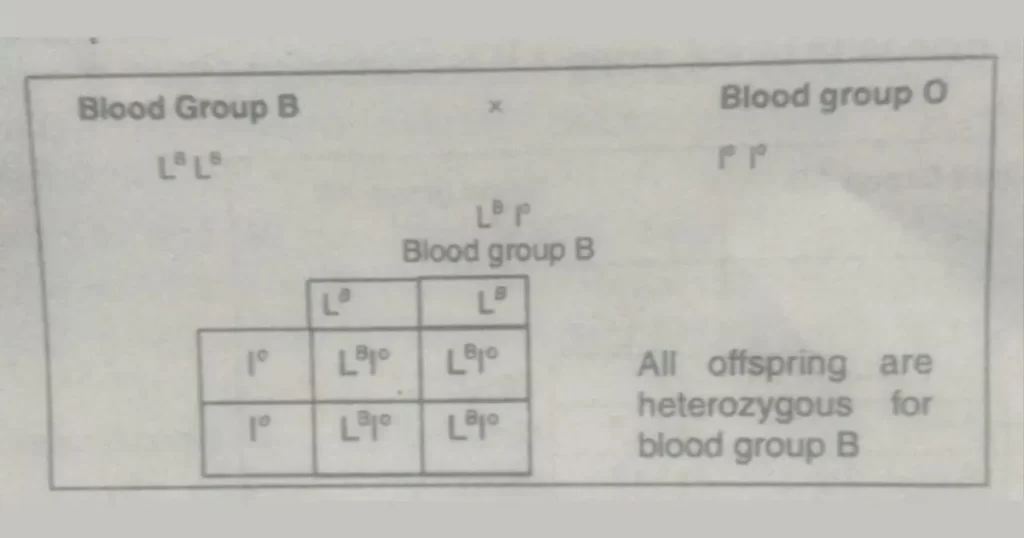
| S. No. | Blood group of parents | Possibilities of blood group in children | Impossibilities in children |
| 1. | A × A | A and O | B and AB |
| 2. | A × B | A, B, AB, O | — |
| 3. | A × AB | A, B, AB | O |
| 4. | A × O | A, O | B and AB |
| 5. | B × B | B and O | A and AB |
| 6. | B × AB | A, B and AB | O |
| 7. | B × O | B and O | A and AB |
| 8. | AB × AB | A, B, AB | O |
| 9. | AB × O | A, B | O and AB |
| 10. | O × O | O | A, B and AB |
If a man homozygous for blood group A marries a woman homozygous for blood group B, all their children will have blood group AB.
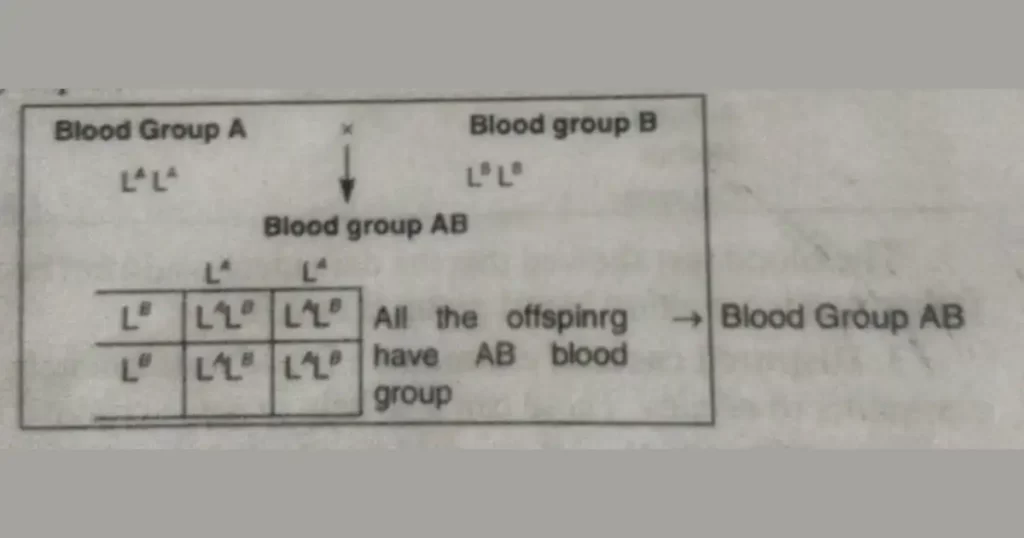
If a man heterozygous for blood group A marries a woman heterozygous for blood group B, their children are of the following four types.
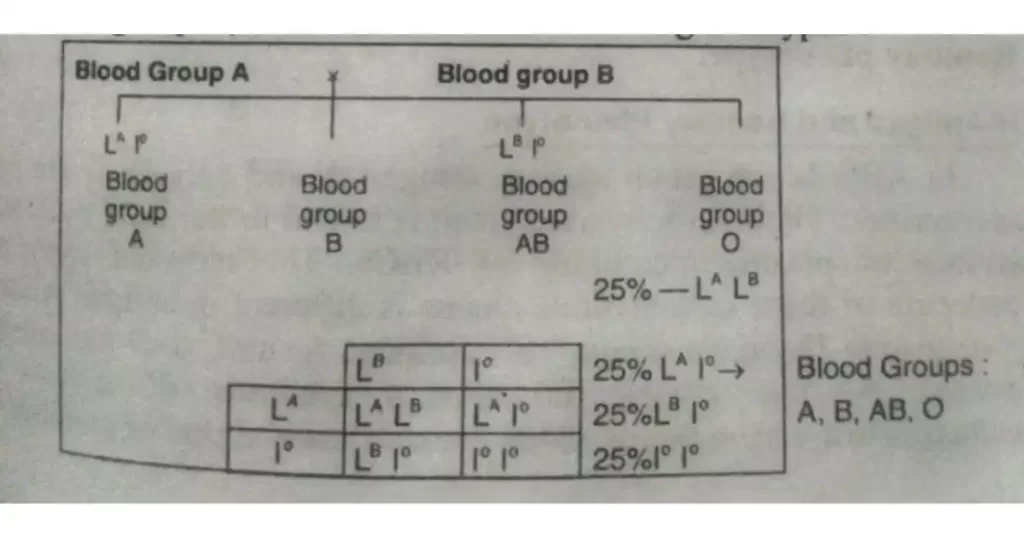
If a man with blood group AB is married to a woman with blood group AB.
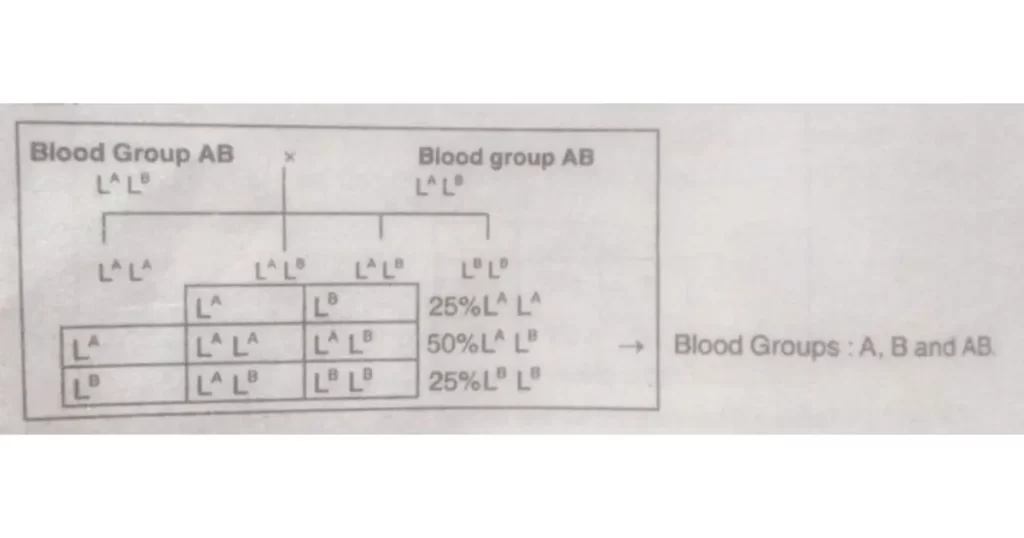
Medico-legal aspects of the ABO series
Knowledge of the ABO blood group is very much helpful in solving cases of disputed parentage and settling the cases of illegitimacy.
- Solution of disputed parentage – Although cases of mixed-up parentage are rare in hospitals, these may happen in some instances and have occurred in the past. Once, two sets of parents took their babies home to a particular hospital at about the same time. Both families discovered it, but Family 2 was not ready for the exchange, in that blood tests se demonstrated the possibility of exchange, and the eschaton satisfied both families.
- Solution of cases of illegitimacy – A widely known movie star in California was accused by a farmer starlet protégé of being the father of her young daughter. The physicians made blood tests of the alleged father, the mother, and the baby with these results.
| Blood Group | |
|---|---|
| Alleged father Mother Daughter | O A B |
The blood test showed that the defendant could not be the father. The real father can have either blood group B or AB.
3. Disputed cases of claimants – Blood tests can help solve claimants’ cases to estates. These can also help in some criminal proceedings.
FAQs of Multiple Alleles
How do multiple alleles arise?
Multiple alleles arise by mutation at the same locus but to different extents.
Define the term pseudo alleles.
Pseudoalleles are functionally related or functionally allelic closely linked genes. These are structurally nonallelic but are inherited together.
What are isoalleles?
Alleles produce the same phenotype effect in a homozygous state but are otherwise different.
Conclusion
So, friends, in today’s article, we studied multiple alleles. Friends, if you do not like this article, please comment and explain your suggestions and mistakes to us.
Thanks