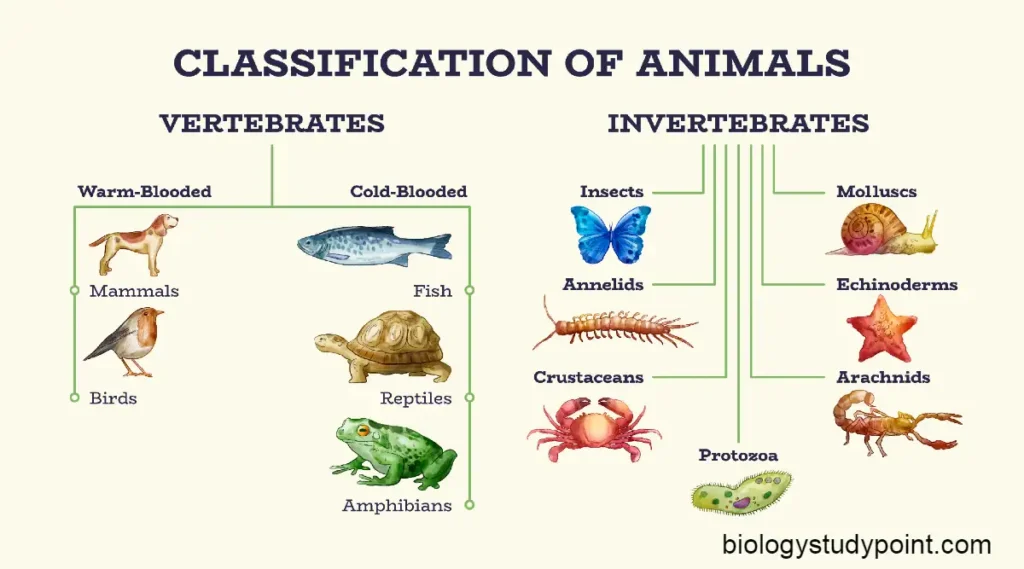
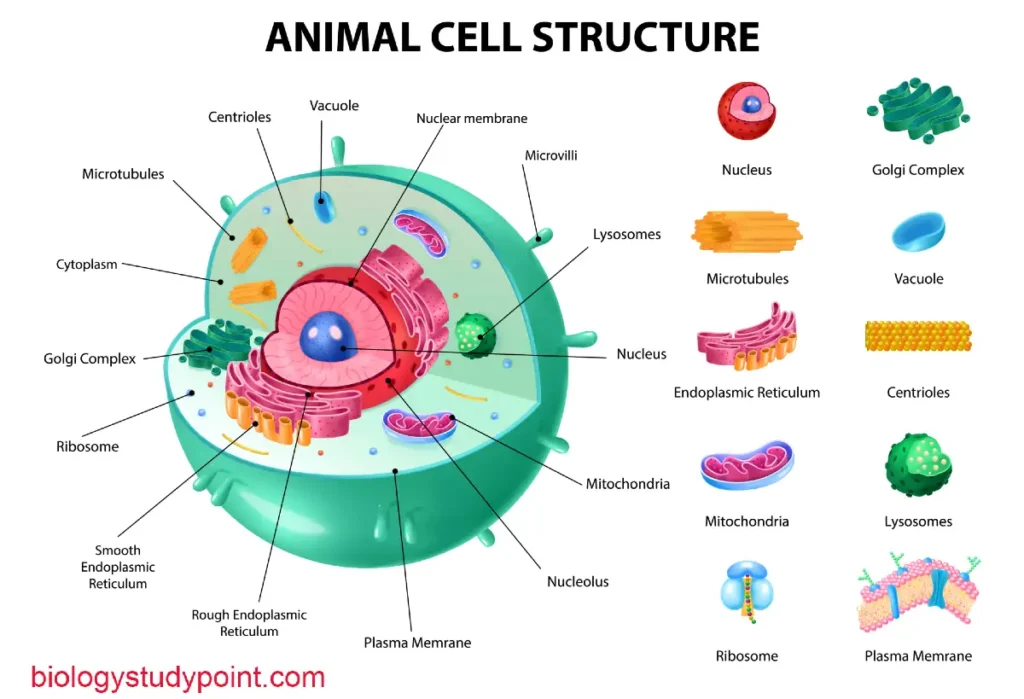
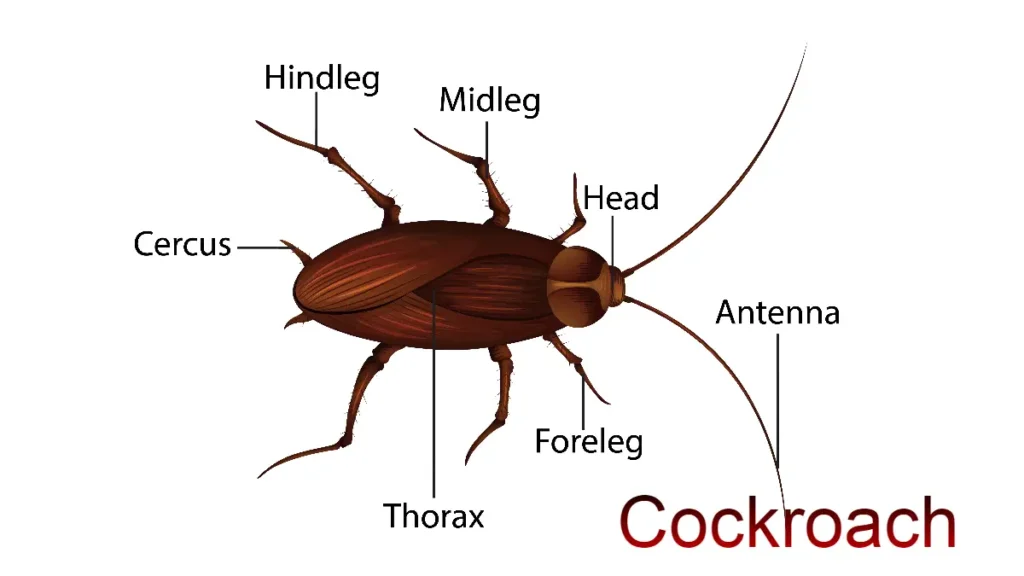
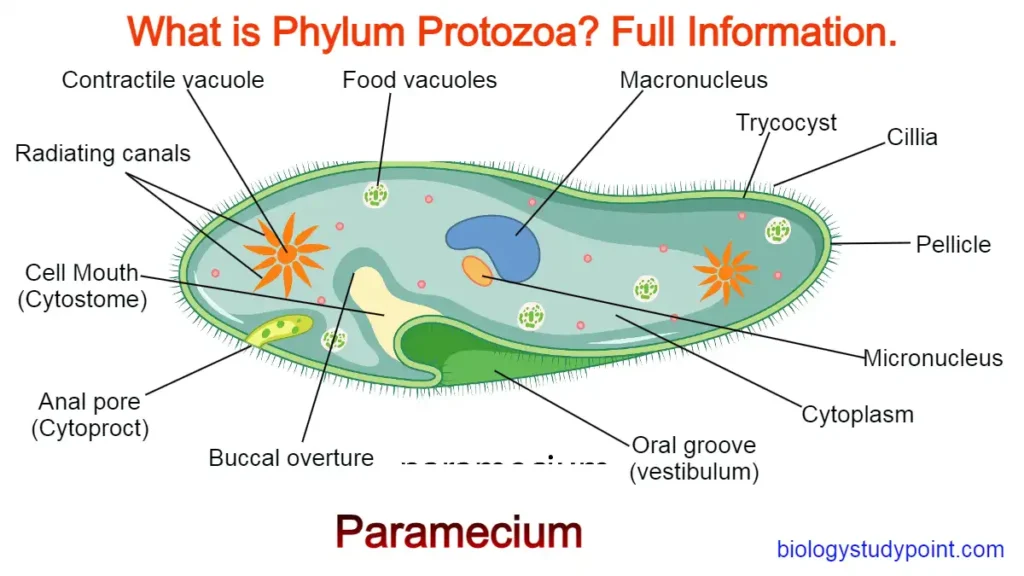
Hello friends, today we are in this article, What is Biotechnology? If we study step by step, friends, without wasting time, start learning.
What is the definition of Biotechnology?
The science of biotechnology includes all industrial processes in which living beings take an active part.
According to the European Federation of Biotechnology – Biotechnology is the biochemistry, chemical engineering, and microbiology undertaking that enables the successful technical use of cultured cells and microorganisms.
We already know the fermentation process by enzymes made by microorganisms, such as making curd from milk, cheese, and vinegar from molasses. This is just an example of biotechnology; there are other examples.
For example – some fungi are used to make antibiotics, etc. All examples are examples of ancient biotechnology. However, the biotechnology developed in the last three decades has been called new biotechnology.
Scope and Importance of Biotechnology
Recent advances in both microbiology and molecular biology have opened up new vistas in the biotechnology field, where microorganisms can be used to produce industrially important biochemicals and enzymes.
This led to a change in the industrial area and the emergence of many biotechnological companies. This also includes gene technology or gene engineering. Gene Cloning and Recombinant DNA under Gene Technology. (rDNA) comes.
In this way, gene technology has become a major area of research today, and some developed countries are increasing the glory of their country by encouraging research in this field.
In our country, India, in the 69th meeting of the Indian Science Congress held in Mysore in 1982, the importance of gene technology was emphasized for the first time.
After this, based on the satisfaction of the Science Advisory Committee of the Parliament, the Indian Government created a separate National Council of Biotechnology under the Department of Science and Technology. This gave it full responsibility for the development of biotechnology in the country.,
After that, the National Council of Biotechnology decided that a list of biotechnology scientists working in the following areas should be prepared.
- Genetic Engineering
- Photosynthesis
- Tissue Culture
- Enzyme engineering
- Alcohol fermentation
- Immuno technology
An “International Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB) was established by the United Nations Council for developing countries, one in India (New Delhi) and the other in Trieste, Italy is it a city named ICGEB’s center that started functioning in India in 1987-88, and since then important research work is being done continuously in this institution? Other centers of ICGEB were also established in India, which are –
- Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi;
- National Dairy Research Institute, Karnal;
- Recently, the name of the Indian Veterinary Research Institute has been changed to “Lal Bahadur Shastri Biotechnology Center.”
Biotechnology and its Branches
Biotechnology is not an independent entity. It is related to many branches of science, such as biology, physics, computer science, chemistry, and mathematics. Therefore, based on technical science, it has been divided into the following branches –
Food Biotechnology
It is concerned with preparing, preserving, and utilizing various food products.
Agricultural Biotechnology
All types of technology are related to improving crops and using organic fertilizers.

Fermentation Technology
It deals with producing alcohol, organic acids, antibodies, enzymes, and biogas by the culture of microorganisms or cells by fermentation method.
Tissue Culture Technology
In this, cells or tissues of animals or plants are chemically cultured.
Industrial Biotechnology
It is related to the commercial production of optional items and optional fermentation technology.
Environmental Biotechnology
In this, waste materials are re-corrected, and polluting substances are purified with the help of microorganisms.
Pharmaceutical Technology
It deals with the production of Interferon, vaccines, Monoclonal Antibodies, Human Growth Hormones, toxoids, etc.
Mine and Metal Biotechnology
It is concerned with the extraction of metals from components and the use of microorganisms in mines.
Recombinant DNA Technology –
It is related to making desired changes in the host DNA by inserting desired genes into the host cell.
Scope of Biotechnology
- Biotechnology is a related science in which work has been done mainly in two areas.
- Molecular Biology.
- Producing technologically essential biochemicals (including enzymes) is a major objective of biotechnology.
- To produce harmless bio-fertilizers instead of chemical fertilizers.
- Production of biopesticides. Production of diagnostic kits for toxoplasmic analysis.
- Production of monoclonal antibodies for transplantation of tissues from organ transplantation.
- Production of xanthine gum for re-beneficiation of crude mineral oils from oil wells.
- Production of transgenic animals and plants, Microbiological production of hydrocarbons.
- Preparation of disease-resistant, high-yielding varieties of crops.
- Given the increasing population, more food must be produced on the available land.
- To produce pharmaceutical products for the treatment of diseases dangerous to humans.
- Preparation of vaccines for the prevention of a disease called Coliavelis (formed in newborn calves).
- The production of plants is effective in photosynthesis.
- Production of ethanol by continuous fermentation.
- Microbiological production of human insulin and interferon (used in leukemia).
- Production of advanced types of vitamin B12.
- Vaccines produced by microbial organisms are highly purified and specific for bacterial, fungal, and viral diseases.
Friends hope what biotechnology is. The information given must have been helpful for you. Friends, if you have any suggestions related to this, please comment.
Thank you