What is connective tissue? How many types are there, and what is its function? You may have many such questions, so today, we will answer them in this article. You must read from beginning to end, and then you will understand well. Without wasting time, let’s start.
What is connective tissue?
Such tissues connect two parts, organs, or areas of our body and are called connective tissue.
Examples – Bone, cartilage, blood, etc. This tissue is made up of Mesoderm.
The function of Mesoderm
It connects two parts of the body and provides circulation. Bones, Cartilage, Tendons, and Ligaments connect organs and support the body. Her blood provides circulation. Circulation means flowing, i.e., conducting.
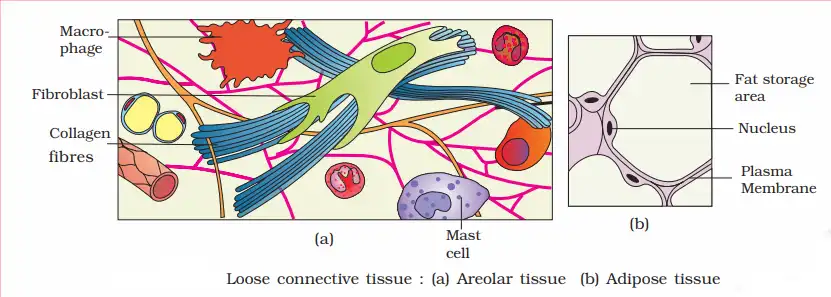
Some special connective tissue cells, called fibroblasts, extract fibers from inside themselves, which come out and are collected.
It is a characteristic of connective tissue. What do these fibers do? They bring flexibility and firmness. Our noses and ears are flexible and firm because of these fibers alone.
Blood is a connective tissue but does not have fibers, so it is an exception to connective tissue. These fibers are of two types: collagen and elastin. Both these types of fibers are secreted by fibroblast cells. The intercellular space is the space between the fibroblast cells where these fibers are found.
How many types of connective tissue?
There are three types of connective tissue.
- Flexible or loose connective tissue
- Dense connective tissue
- Specialized connective tissue
1- What is flexible/loose connective tissue?
Tissues have large spaces between the fibers and the fibroblast cells. This means they are a little far apart, which makes them loose-fitting. Hence, they are called flexible or loose connective tissue.
Examples – Areolar tissue, Adipore tissue, etc.
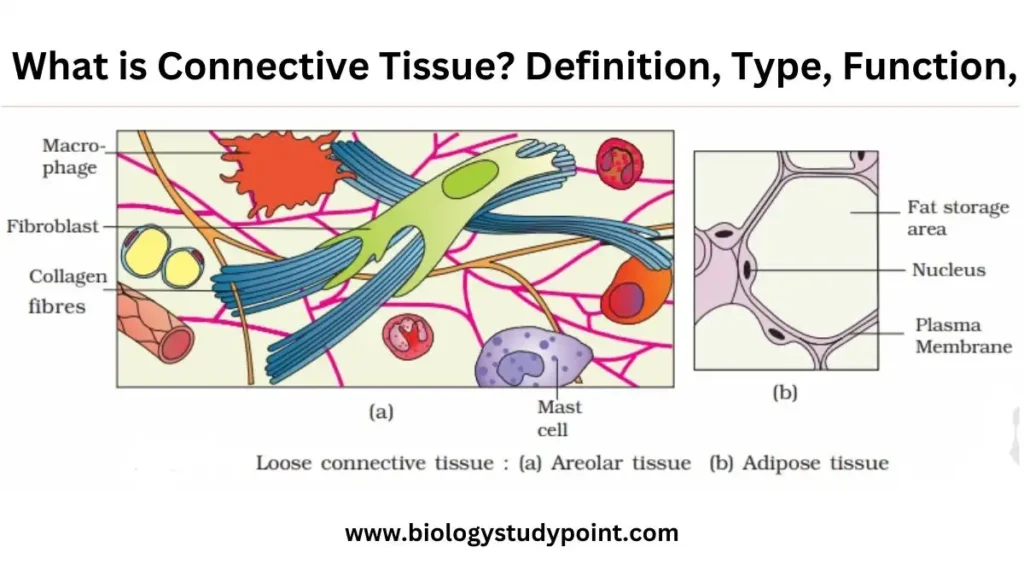
What is Areolar tissue?
- It is found under the skin.
- Gives support to the skin.
There are three types of cells in this tissue. Mast cells, phagocytes, and fibroblast cells. Let’s see what these cells do. Let’s assume that our skin is peeled a little, and microorganisms from the outside enter the inside when it is peeled. The. The harmful organisms microorganisms are eaten or destroyed by the phagocytic cells Whe. Saved from these, the mast cell, which is there, extracts a hormone called histamine, and this hormone swells the blood vessel of the place where there is an injury, which causes more blood to start collecting there. The. The temperature increases because Our blood gets warm, and harmful microorganisms die due to high organisms.
What is adipose tissue?
The tissues that store fat in our body are called adipose tissue.
These are also found under the skin.
Some animals have a thick layer of fat under the skin called blubber. SuThesereatures are found in icy regions, and this layer preserves their body temperatures to survive evetheyemperatures.
Example – Seal.
2- What is dense connective tissue?
Dense connective tissue is tissue in which the filaments and fibroblast cells are firmly attached. There are two types.
- Dense regular connective tissue
- Dense irregular connective tissue.
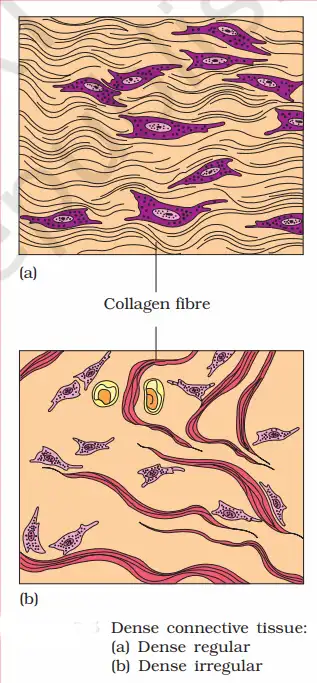
Dense regular connective tissue—In this tissue, the fibres are arranged in a regular arrangement and parallel to each other; hence, they are called dense regular connective tissue.
Example – Tendon, ligament, etc. The function of tendons is to connect muscle to bone, and the function of ligaments is to connect bone to bone.
Dense irregular connective tissue—The fibers in this tissue are arranged irregularly, tissue.
Example: They are found under the skin, and in the eyes, a sclera layer is under the retina.
3- What is Specialized connective tissue?
There are two types of Specialized connective tissue.
Skeletal connective tissue – These tissues support the body and are of two kinds.
- Cartilage
- Bones
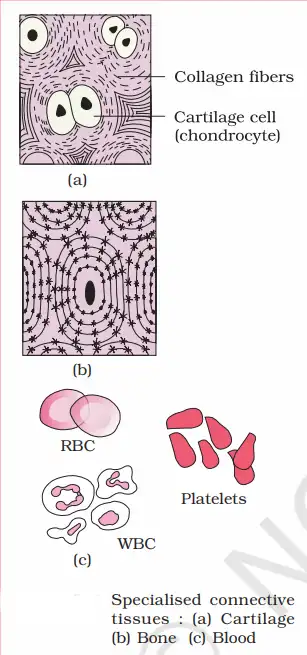
What is Cartilage?
It is slightly flexible. Regarding its structure, its outer covering is called the perichondrium, and its cells are called chondroblasts. When these chondroblasts mature, they become chondrocytes.
This chondrocyte forms a matrix with an empty vacuole called a lacuna. In this one lacuna, there are 1-4 chondrocytes, and the substrate in it is called chondrin. This chondrin is rigid, particularly pliable, and anti-spinning. Specific flexible means bending or flexibility, and anti-spindle means returning to its original position after turning.
For example, If we leave our earlobe after folding it, it returns to its original position.
Example – Where is this cartilage found? In the tip of the nose, the ears, the middle of the spinal cord, etc.
What is the study of cartilage?
The study of cartilage is called Chondrology.
What are the bones?
The study of bones is called Osteology, and the formation of bones is called Osteossification. Bone is the most complex tissue. Along with this, the bones in the body are called osteoblasts. The cells that are maturing are called osteoblasts. About the structure of bone, its outer cover is called the Periosteum. It also has a matrix and lacuna, but only one cell or osteocyte is found in its lacuna, while one to four cells are in it.
Its matrix contains collagen and calcium ions, which together provide firmness. It has no specific flexibility. It supports and protects the body and forms a protective framework for soft organs.
What is fluid connective tissue?
Fluid connective tissue performs the function of circulation in the body. There are two examples of this.
- Blood
- Lymph
What is blood?
Blood is a red liquid connective tissue. It is red because it contains a red pigment called Hemoglobin. TheHemoglobin. The amount of blood in a healthy adult human’s body is about 5 to 5.5 litres, and the amount of Hemoglobin in it is 12 to 16 grams / 100 ml.
Females have 12 – 14 g / 100 ml, and males have 14 – 16 g / 100 ml. Females have less haemoglobin because they have a menstrual cycle or period every month, during which they lose a lot of blood.
Components of blood – Two types of components are found inside the blood.
- Plasma
- Organized substance
Also, read –
What is the animal kingdom? Complete notes.
What is the plant kingdom? Full Information.
What is biology’s definition and branches?
What is a cell wall? Complete notes
What is plasma?
It is found in 55% of our blood. It is a colorless blood component and contains 90-92% water, the rest being organic matter and inorganic matter. Inorganic substances contain ions. The organic matter comprises plasma proteins, digested food substances, nitrogenous waste products, clotting factors, and antibodies.
Plasma proteins include albumin, globulin, fibrinogen, and prothrombin. Albumin controls blood osmotic pressure, globulin helps with immunity, and fibrinogen acts as a prothrombin clotting factor.
What is organized substance?
It is found in 45% of the blood and includes red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets. RBCs are also called erythrocytes, in which erythro means red and cytes means cell.
Similarly, WBCs (White Blood Cells) are called Leukocytes, in which Leuko means white and Cytos means cells. Similarly, platelets are called thrombocytes, where thrombi mean clot and cytosol means cells.
Red Blood Cells (RBCs) –
It is red because it contains a red pigment called HemoglobinHemoglobin. In adult and healthy men, the quantity of RBCs is 4.5 – 5.5 million/mm3. However, for small children (infants), the amount is 6 -7 million/mm3. That’s why the cheeks of small children look pink.
When talking about the shape of RBCs, when they are immature, they are round, and all the organelles are present. However, when they mature, they become biconical, and all the organelles inside them are destroyed so that the maximum amount of HemoglobinHemoglobin can come inside it. The primary function of RBCs is to transport gases (O2 & CO2); the more Haemoglobin there is, the more gases are exchanged.
White Blood Cells (WBCs) –
These are 6000 – 8000/mm³ in the blood. It is of two types.
1—Granulocytes—These are called granular because small particles are found along with the nucleus in their cytoplasm. There are three types.
Neutrophils – These are phagocytosis. Neutrophils make up 60-65% of the total WBCs.
Basophils make up 0.5-1% of the total WBCs. Three chemicals, histamine, serotonin, and heparin, emerge from these. These cause allergic reactions, and all allergic reactions are due to histamine and serotonin.
Eosinophils – It makes up 2-3% of the total WBCs. These cells are responsible for inflammatory reactions. For example, when pricking a thorn somewhere, the temperature of the skin increases, swelling occurs, it becomes red, and there is pain.
2—Agranulocytes—This is of two types; only the center is found; particles are not found.
Monocytes – It makes up 6-8% of the total WBCs. These are also phagocytic cells.
Lymphocytes – It makes up 20-25% of the total WBCs. It produces antibodies.
Platelets—Platelets are also called platelets. Their function is blood clotting, and they are 1.5 – 3.5 lac/mm³ in normal adult humans. When the number of platelets decreases, coagulation-related diseases occur.
What is Lymph?
It is pale yellow or colorless because it does not contain RBCs. Lymph also contains plasma. Its plasma components are similar to those of blood plasma, with the only difference being that the plasma component of lymph has more glucose and less protein. In comparison, the plasma component of blood has less glucose and protein, and the quantity is more significant. Lymphocytes and some WBCs are also found in the lymph.
Friends, I hope you have liked the information about connective tissue; if you like it, share it with your friends so that they can benefit from it. If you ask me in this article, but if there is a mistake, please tell me by commenting.