Friends, if you want to know completely about DNA, if yes, from your side, then this article is for you; if you read this article completely, you will get a lot of information about DNA. So, without wasting any time, let’s start.
What is DNA, and where is DNA located?
DNA is a Genetic material found in the cells of Living organisms, except for plant viruses and a few animal viruses, which form the genetic material in Eukaryotic cells. DNA occurs in the nucleus and, together with protein, forms chromatin. Traces of DNA are also found in mitochondria and chloroplasts.
What is the Full form of DNA?
DNA – Deoxyribonucleic acid.
Who Discovered DNA?
Swiss chemist Johann Friedrich Miescher, in 1869, was the first to identify DNA.
What is the structure of DNA or Morphology?
DNA is a long, spirally twisted, unbranched thread in eukaryotic cells. It is circular in mitochondria and plastids of Eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells.
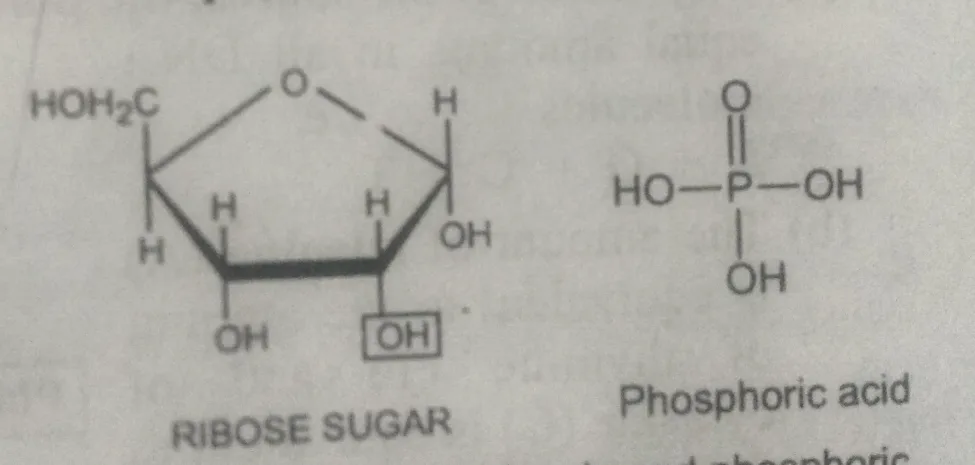
What is the chemical composition of DNA?
Composed of three types of compounds:
- Sugar – It is a pentose sugar, the Deoxyribose.
- phosphoric acid
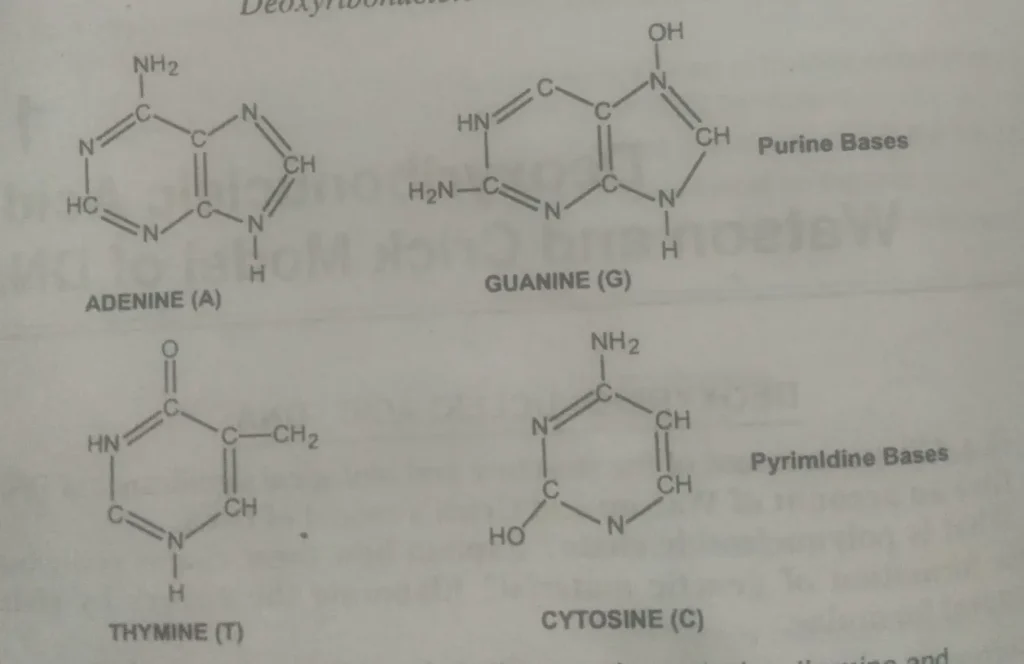
- Nitrogenous bases –
Nitrogenous bases –
These are nitrogen-containing organic ring compounds. There are four types: (A:) adenine, (B) thymine, (C) cytosine, and (D) guanine. These four nitrogenous bases are of two different types:
Purines and Pyrimidines
What are purine bases?
Purines –
Adenine and guanine are two purines found in DNA. Represented by the letters A and G. These are two-ringed nitrogen compounds.
What are pyrimidines?
Pyrimidines –
Cytosine and thymine are the Pyrimidines. These are formed of one ring only. These are represented by the letters capital C and T.
What is the molar ratio of nitrogenous bases in DNA?
Chemical analysis reveals three fundamental features of DNA.
(a) Regardless of the source, the parent remittance components occur in equal amounts in all DNA molecules, i.e.
A + G = C + T
(b) The amount of adenine (A) is equivalent to the amount of thymine (T), and cytosine (C) is comparable to that of guanine (G), i.e.,
A = T and G = C
(c) The base ratio A = T/G = C may vary in the DNA of different groups of animals but is constant for a particular species. Therefore, this ratio has been used to identify the DNA from a specific source.
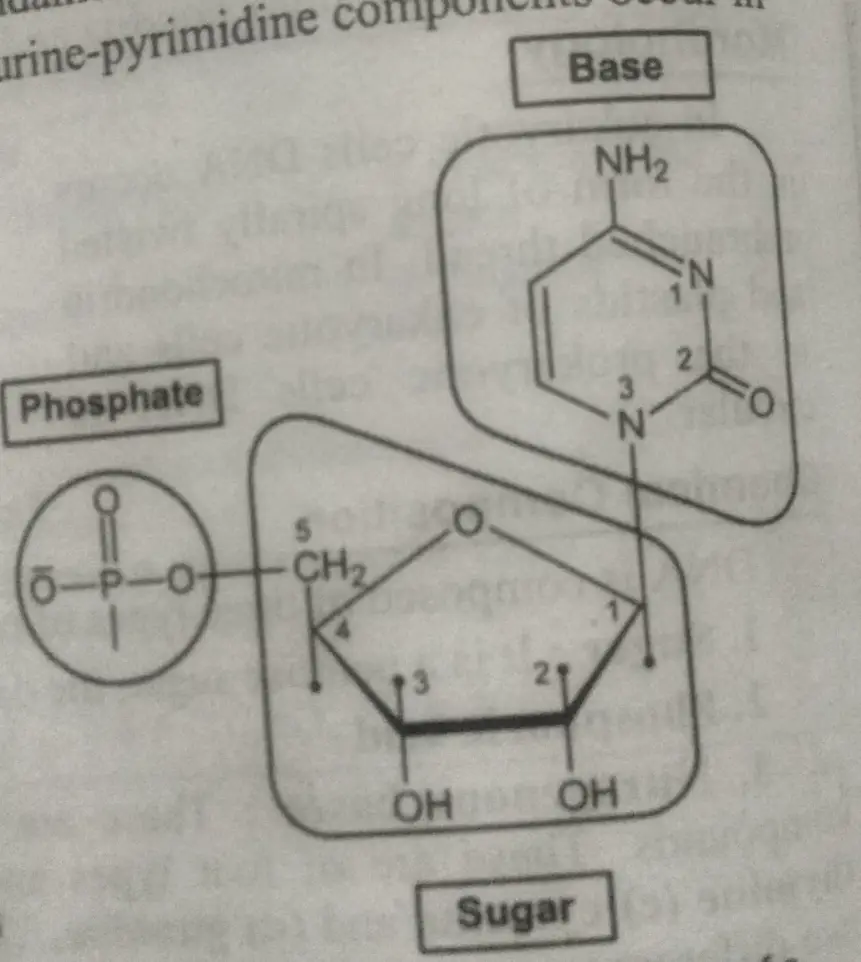
Molecular structure of DNA
DNA is a macromolecule. Its nitrogenous base joins with Deoxyribose to form nucleosides and with the Deoxyribose and phosphoric acid to form nucleotides.
- Nucleosides –
A nitrogenous base with a Molecule of Deoxyribose (without phosphate group) is known as a nucleoside. In a nucleoside, the first carbon atom of Deoxyribose is linked to the first nitrogen (in pyrimidines) or the 9th nitrogen (in purines). Thus, there are nucleosides in a DNA molecule. These are:
Adenosine – Adenine + Deoxyribose
Guanosine – Guanine + Deoxyribose
Cytidine – Cytosine + Deoxyribose
Thymidine – Thymine + Deoxyribose
- Nucleotides –
A nucleotide comprises one molecule of Deoxyribose, one molecule of phosphoric acid, and one of the four nitrogenous bases. The phosphoric acid molecule is attached to the 5th Carbon atom of the deoxyribose ring. Since there are four nitrogenous bases, there are four types of nucleotides.
Deoxyadenylic acid – Adenine + Deoxyribose + Phosphoric acid.
Deoxyguanylic acid – Guanine + Deoxyribose + Phosphoric acid.
Deoxycytidylic acid – Cytosine + Deoxyribose + Phosphoric acid.
Deoxythymidylic Acid – Thymine + Deoxyribose + Phosphoric acid.
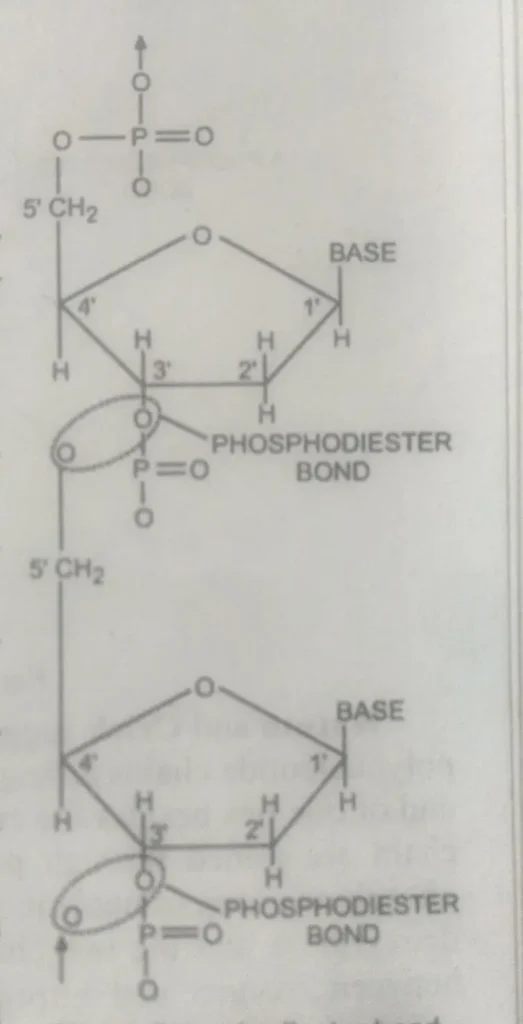
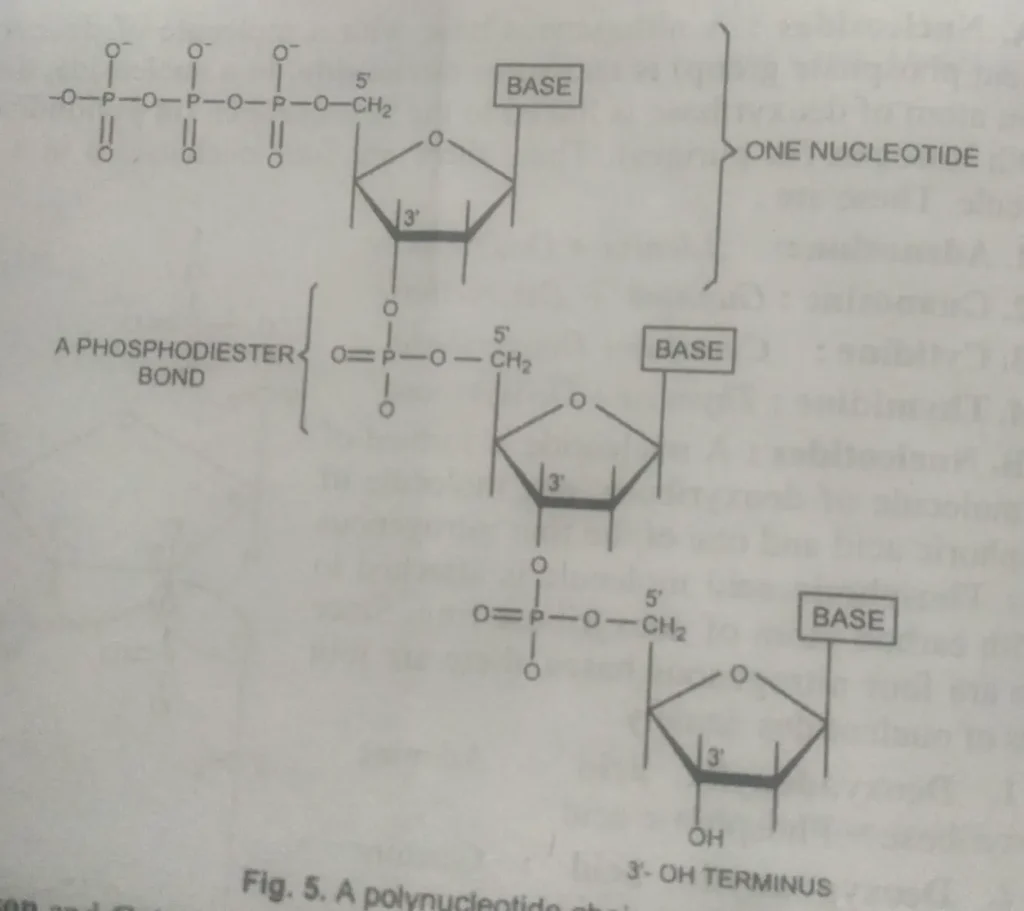
- Polynucleotide chain –
DNA is a macromolecule with a very high molecular weight. Its monomers are nucleotides, which are linked in a specific fashion to form a polynucleotide chain.
In a polynucleotide chain, the adjacent nucleotides are connected by a Phosphodiester bond between the phosphate molecule of one nucleotide and the third carbon atom of the sugar molecule of the other nucleotides.
This form is the sugar-phosphate chain. The nitrogenous base is attached to the first carbon atom of Deoxyribose and is directed at 8 at right angles to the long axis of the polynucleotide chain.
One End of the polynucleotide chain has sugar residue with C-3, which is not linked to another nucleotide, and the other End has sugar residue, C-5, which is not linked to another nucleotide. These are named 3′ and 5′ ends, respectively.
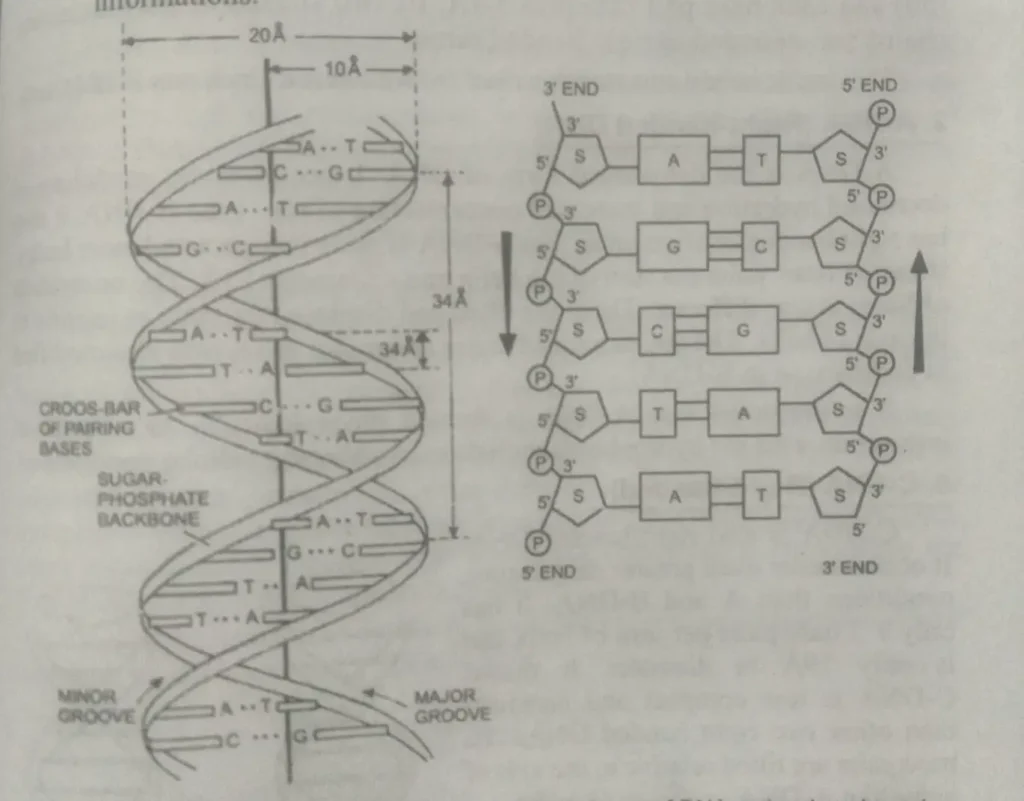
Watson and Crick’s model of DNA
In 1953, D.S. Watson and F.H.C. Crick presented a working DNA model. The Watson and Crick model of DNA illustrates its chemical nature and the mechanism by which it duplicates itself.
Watson and Crick suggested that in a DNA molecule, two such polynucleotide changes are arranged, and two parallel are in the opposite direction so that 3 ends of one lie beside the End of the other. The adjacent nucleotides of each chain are joined through phosphodiester bonds.
In such a structure, the phosphate group of nucleotides in each chain Rs trend lies on the outer side of Deoxyribose. The two chains are linked through hydrogen bonds formed Between oxygen and nitrogen atoms of adjacent nitrogen as bases. The unique feature of pairing between bases is :
- Purines (adenine and guanine) Pair with Pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine) and
- Adenine pairs with thymine, and guanine pairs with cytosine.
DNA consists of two complementary chains twisted around each other. One turn of The Helix measures about 34 angstroms. It contains 10 paired nucleotides placed at regular intervals of 3.4 angstroms.
The diameter of The Helix is roughly 20 angstroms. A narrow and wide helical groove is the space between successive turns when the pair is wound into a helix.
What is the role of DNA in Heredity?
- DNA is the chemical basis of heredity. Its significance is heredity as follows:
- DNA replicates itself accurately.
- DNA can have a sufficiently stable structure and is least liable to mutations or heritable changes.
- DNA has the potential to carry all kinds of necessary biological information.
- DNA can transmit or translate this information to the cell. Inside the cell, specific proteins are synthesized to control the expression of a character.
How many forms of DNA? or How many types of DNA?
Describe the molecular structure of different forms of DNA.
Under different isolation purification and crystallization conditions, 6 different forms of DNA double helix have been identified. Some of these forms are interconvertible. The differences in this DNA formed are based on:
- The number of base pairs present in each turn of the DNA helix.
- The pitch or angle between each base pair.
- The helical diameter of the DNA molecules.
- The right or left-handedness of the double helix.
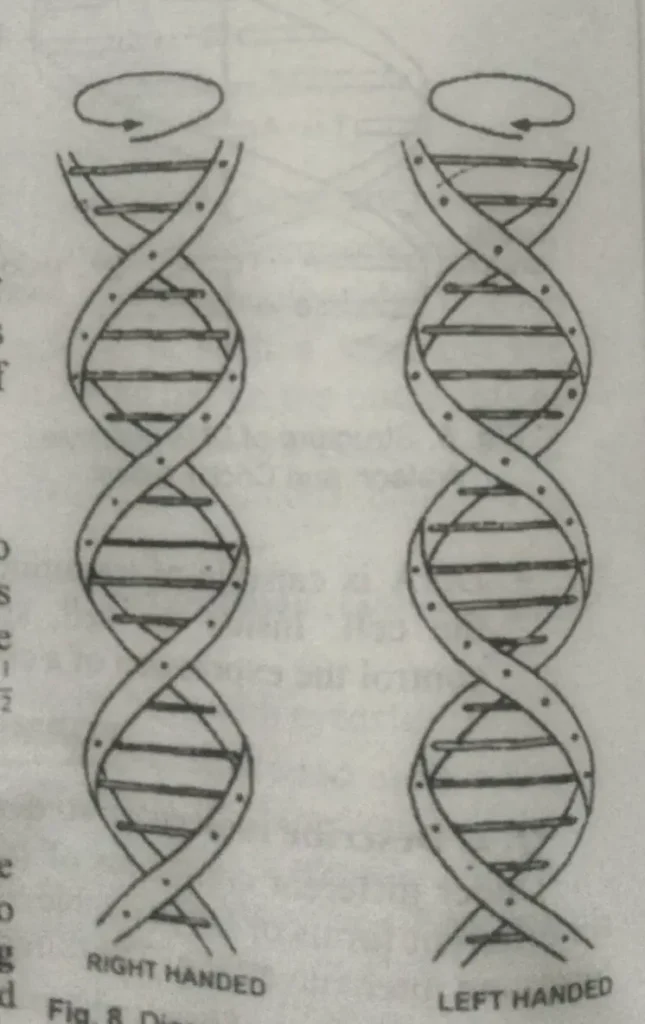
- B DNA (right-handed DNA)
- A-DNA (Right – handed DNA)
- C-DNA (Right-handed)
- D-DNA
- E-DNA
- Z-DNA (Left-handed DNA)
- B DNA (right-handed DNA) –
This form of DNA occurs in all living beings and begins under normal conditions, i.e., under low salt concentration and a high degree of hydration.
Each coil or turn measures 34 Angstroms or 3.4 nm. Each turn has 10 base pairs (bp), and each base pair occupies 3.4 Angstroms. Its two strands or polynucleotide chains are wounded in right-handed turns.
- A-DNA (Right – handed DNA)
A- DNA is the dehydrated form of DNA. It occurs under conditions of decreased hydration and increased concentration of Na. Like B-DNA, it also has a right-handed configuration, but A-DNA is more compact and bulky. It has 11 base pairs per turn of the helix and a diameter of 23 Angstroms.
The orientation of bases is also different. These are tilted and displaced laterally about the axis of the helix. The appearance of major and minor grooves is also modified compared to B-DNA.
A-DNA is presumed physiologically formed due to interaction with the hydrophobic molecules in changing cellular conditions.
- C-DNA (Right-handed)
C-DNA is also right-handed DNA. It occurs under even greater dehydration conditions than A and B-DNA. It has only 93 base pairs per turn of the helix and is only 19 Angstroms in diameter.
C-DNA is less compact and narrower than the other two right-handed DNAs. Its base pairs are tilted relative to the axis of helix-like A – DNA.
- D-DNA and E-DNA
These two forms of DNA are also right-handed. They occur in helices that lack guanine in their base composition and have 8 and 7.5 nucleotides per turn, respectively.
- Z-DNA (Left-handed DNA)
Z-DNA is left-handed DNA. The phosphodiester backbone of its two polynucleotide strands follows a zig-zag course, which is why it is called Z-DNA.
The helix of Z-DNA is 18 angstroms in diameter and contains 12 base pairs per turn. The major groove present in B-DNA is nearly absent in Z-DNA. Thus, Z-DNA is more compact.
Because of this compactness, the phosphate groups on opposite strands of Z-DNA are closely placed and create a greater electrostatic repulsion.
Thus, Z-DNA is energetically less stable. Z DNA is formed only when purines and pyrimidines are present alternately in the polynucleotide chains.
Z – DNA was discovered by Wang and Rich in 1979. Z DNA configuration appears when DNA is brominated or methylated, and it can be stabilized by high salt concentration after specific cations.
Antibodies that recognize and bind specifically to Z DNA can demonstrate the existence of Z DNA in Drosophila.
What is the DNA replication process?
During DNA replication, the weak hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases of the nucleotide separate so that the two polynucleotide chains of DNA also separate and uncoil. The chains thus separated are complimentary to one another.
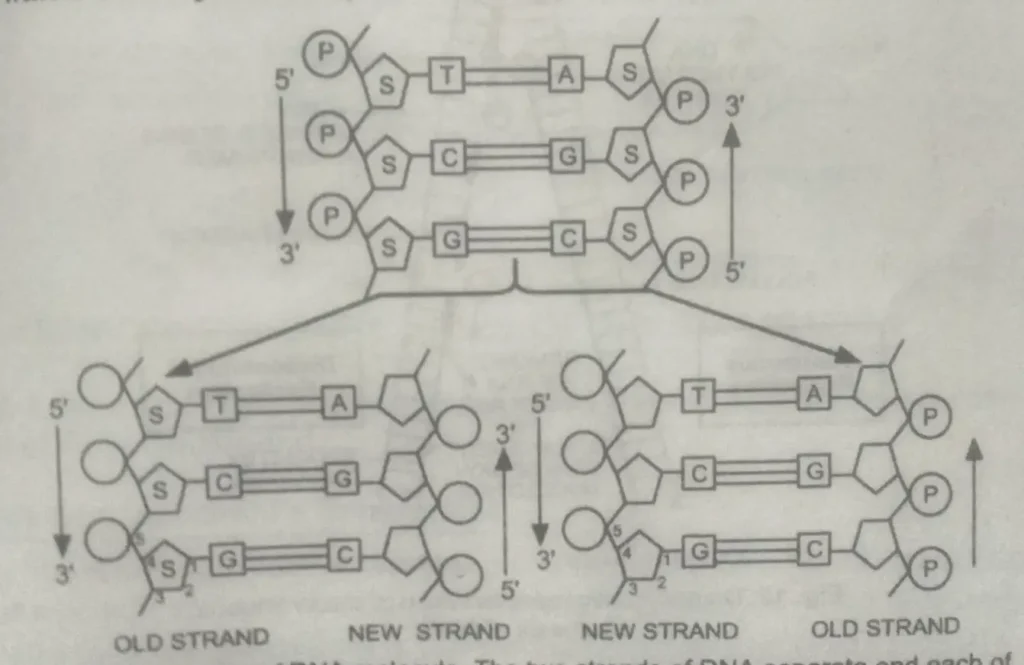
Because of the specificity of base pairing, each nucleotide in separated chains attracts its Complementary nucleotide from the cell cytoplasm.
Once the nucleotides are attached to sugar radicals by their hydrogen bonds, they unite through their phosphate components and form.
Thus, each chain of the double helix of DNA serves as a template or model for its complementary chain.
This method of DNA replication is described as semi-conservative because each daughter DNA molecule is a hybrid that conserves one parental polynucleotide chain and synthesizes the other.
Enzymes for DNA synthesis –
Two enzymes are necessary for DNA synthesis
DNA polymerase and polynucleotide ligase
DNA polymerase has three sites for attachment. One of them attaches to The template DNA, The second to The triphosphate nucleotide, and the third one to the 3’-OH End of the DNA primer.
Thus, DNA polymerase adds triphosphate nucleotide to primer DNA from the 5′ end to the 3′ end of the polynucleotide chain. The new strands are synthesized in fragments, which the enzyme polynucleotide ligase joins.
Why is DNA replication called discontinuous?
Okazaki suggested that DNA synthesis proceeds simultaneously on both strands. The 3′ – 5′ strand of DNA is called the leading strand. On this strand, the new polynucleotide strand is synthesized in one piece in a 5′ – 3′ Direction. The 5′ – 3′ strand of DNA is called the lagging strand.
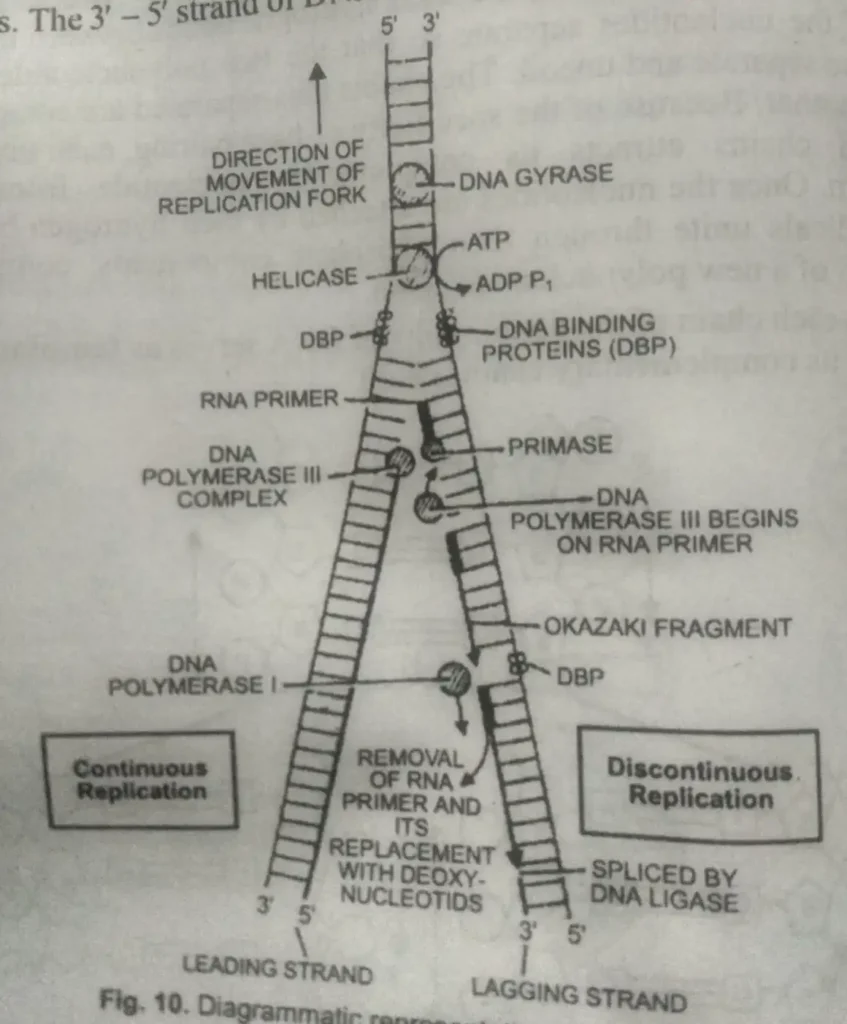
On this strand, the new polynucleotide strand is synthesized in a 5′ – 3′ direction in the form of small isolated segments utilizing the same enzyme. These segments are known as Okazaki pieces, consisting of 1000-2000 nucleotides.
The enzyme polynucleotide ligase joins these together, completing the formation of polynucleotide chains. Autoradiographic experiments support the discontinuous synthesis of DNA.
What are the Unidirectional and bidirectional replication of DNA?
J. Cairns concluded from his experiments that DNA synthesis starts at a fixed point on the chromosome and proceeds in one direction, but recent experiments suggest bidirectional replication.
Levinthal and Cairns Proposed that during replication, the two strands do not separate; instead, they start to end at one End, and simultaneously, the unzipped segments start attracting the respective nucleotide Pairs.
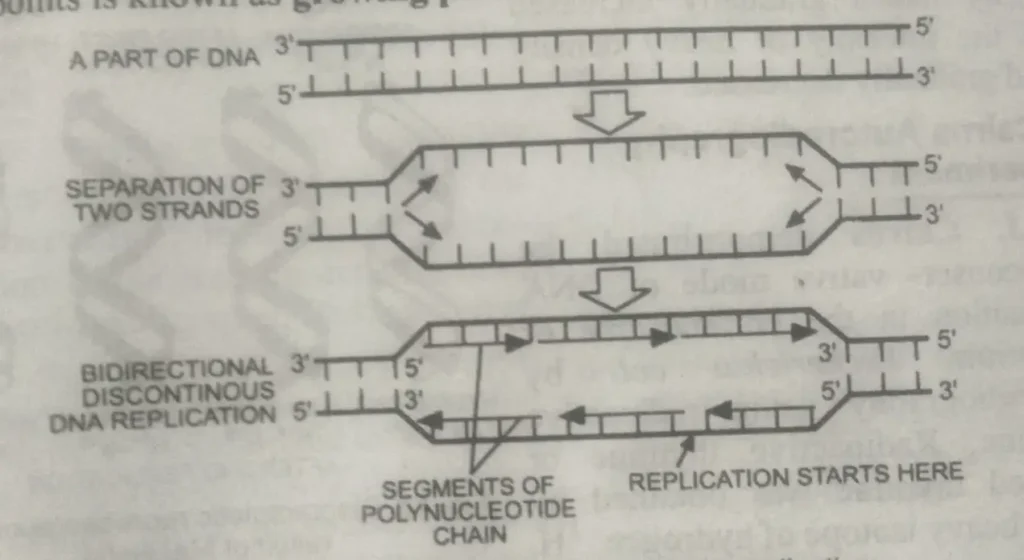
This way, unzipping the original DNA strands and synthesizing fresh DNA strands go side by side. This means that in duplicate DNA, a Y-shaped growing point must be visible.
Cairns has demonstrated two Y-shaped regions in the circular replicating DNA of bacteria. One of these points is known as the growing point, and the other is the initiation Point.
What sugar is found in DNA?
Yes, sugar is pentose sugar or Deoxyribose.
Friends, I hope you have liked the information about DNA; if you like it, share it with your friends.
Thank you