Hello, friends. Today, we will read in this article what the Root is and what the function of roots is, so let’s start without wasting time.
What are flowering plants?
Such plants in which flowers are found are called flowering plants. They are also called angiosperms.
The flowering plant is divided into two parts from the externals.
- Root system
- Shoot system
In this article, what is the Root? I will study it completely.
What is the root system?
Root system –
The part of the underground plant is called the root system, and many roots together make up the root system. But there are some plants whose stems have been modified and are found underground. For example – potato, ginger, colocasia, etc.
How is the Root formed? Or how is the root system formed?
Now, we will know how this root system is formed and what things it is made up of. See, the root system is made up of roots, and we understand how these roots are made.
The plant is formed from one or the other seed, and on top of this seed, there are two coverings, which are called seed cover or seed shell. Now, an embryo is found inside this seed, and cotyledons are found in this embryo. The embryo that has two cotyledons is called a Dicot, and the embryo that has one cotyledon is called a Monocot.
What is the function of cotyledon?
Now you will think about the work of this cotyledon; see, nutritious substances are stored in this cotyledon, and then this cotyledon has some structures or cells in the embryo that work to provide nutrition during development. These structures are called Plumules and Radicle. Now it comes to the point of what these Plumules and Radicle do.
See, when the seed is put in the soil, the water in the soil enters through a hole in the seed called a seed gate, and when the water enters, the seed coat bursts due to the pressure of the water, and when the seed coat bursts, the embryo comes in contact with the soil. By getting the mineral elements and water present in the soil, the plumules and radicles present in the embryo develop. They start doing this, out of which the plumules later form the stem, and the radicle forms the Root.
Now, first of all, we will read about the Root, so let’s read.
What is the Root?
The part or structure that is formed from the radicle is called the Root. It is of three basic types.
- Taproot
- Fibrous Root
- Adventitious Root
What is the taproot?
This Root is mostly found in Dicot. Now, it comes to the question of how this taproot is formed. See, when the seed is put in the soil, the inside of the seed gets burnt, due to which its cover bursts due to the pressure and when the cover bursts, its embryo comes in contact with the soil, and the soil contains mineral elements called After getting there, the plumules and radicle present in the embryo start developing.
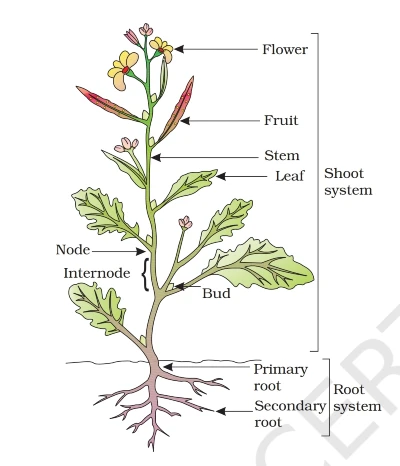
The plumules grow upwards to form a stem, and the radicle grows downwards to create a thread-like structure, which is called the primary Root. Now, some branches emerge from this primary Root, which is called the secondary Root. The branches that arise from this second Root are called tertiary roots. So much of the whole structure is called tap root. That is, the primary Root and its branches together form a single root, which is called a tap root.
Example – Mustard plant etc.
What is a fibrous root?
It is mostly found in monocots. Now, it comes to the question of how fibrous roots are formed. See, in this also the seed is put in the soil, after that the water goes inside, then the cover bursts and after that the plumules grow and first forms a small stem which is called the plantlet. And at the same time, the radicle also grows to form the primary Root. So far, the bean process is like the taproot.
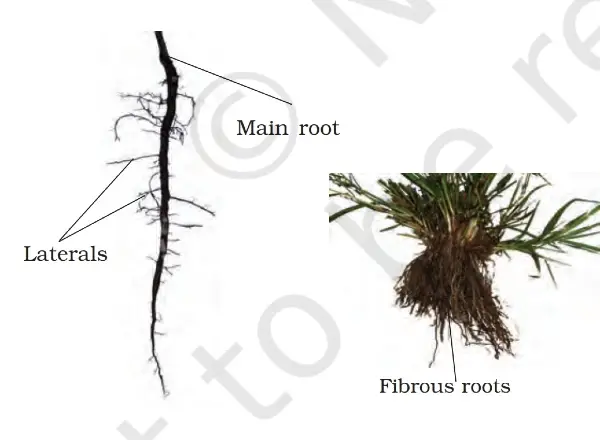

But after this, the stem grows a little, and the primary Root also grows a little; after that, this primary Root gets destroyed after some time (in a short life). After that, many structures emerge from the base of the stem in the form of fibres, which are called Fibrous roots, to support this stem.
Example – Wheat plant etc.
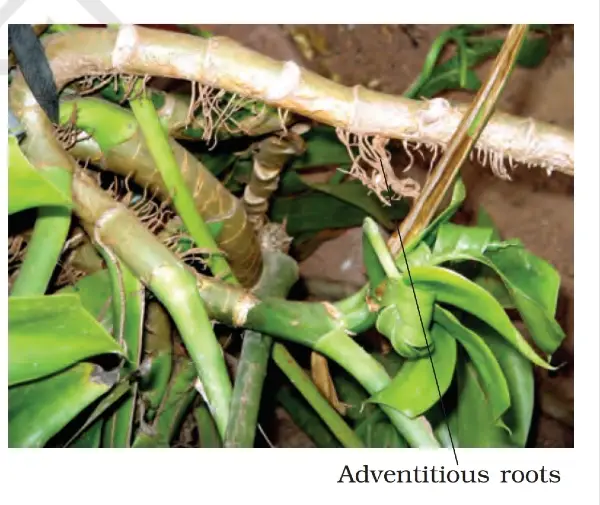
What is the adventitious Root?
Such roots that grow from any part of the tree without coming out from the radicle are called adventitious roots. This Root is found in both monocots and dicots. We will understand this with an example.

Examples – Banyan tree, sugarcane plant, etc.
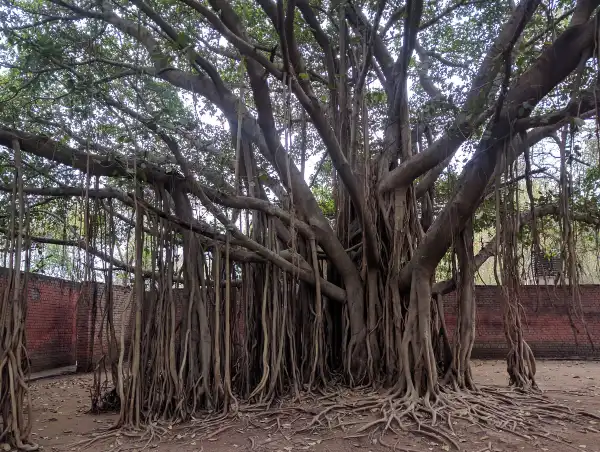
You must have seen the banyan tree. Taproot is found in the banyan tree, and the branches that have come out from the trunk of this tree must have been seen hanging down from those branches. The rope-like Root slowly grows and sinks into the ground. These roots are called prop roots, which is an adventitious Root. The banyan tree is huge, and this prop root provides basic support for it.

The fibrous Root is found in the sugarcane plant. You must have seen sugarcane. You must have seen that knots are found in sugarcane at some distance; this knot is called a node. The part between these knots from which we chew and extract the juice is called Internode.
This sugarcane plant is weak and tall. Now, to support this sugarcane, fiber-like roots emerge from the knot at the base and sink into the ground. These fibrous roots are called stilt roots, which is an adventitious Root.
Modification of Root
Let us first talk about what modification of the Root means. See, the meaning of modification is to change from one form to another, and we are talking about the Root here. See, the main function of the Root is to absorb water and mineral substances and provide support to the plant, but in some plants, it changes its shape and structure to perform other functions as well.
For example, when storing food, it transforms itself for respiration.
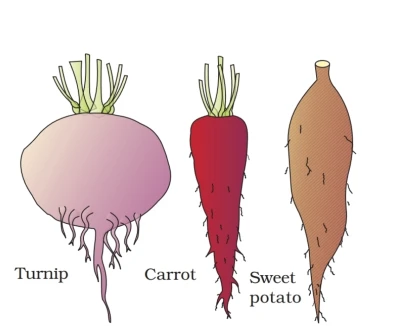
Examples – Carrot, turnip is a tap root, and sweet potato is an adventitious root.
Region of roots –
Four regions are found in the Root. To protect the top part of the Root, which sinks into the soil, a structure is formed, which is called a root cap or soft cells present in the region of meristematic activity, which protects the part from destruction. He is called Root Cap.
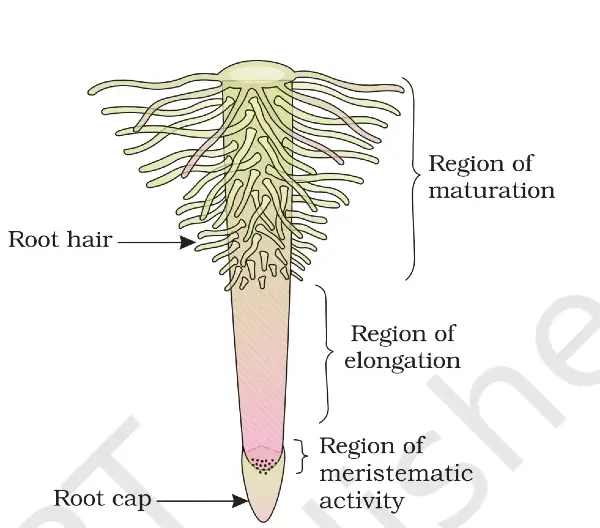
Region of meristematic activity: The region near the root cap that contains meristem cells is called the region of meristematic activity. It continuously divides to form another region called the region of elongation, and when meristematic cells divide again and again, these cells grow in length.
After that, the old cells of the region of elongation, which mature while moving upwards, form another zone near it, which is called the region of maturation. Thread-like structures emerge from this region, which are called root hairs. These root hairs absorb water and minerals.
What is the shoot system?
The above-ground part is called the shoot system. Why it is called a system because it is made up of many things like – what is being found outside the ground, the stem being seen outside and branches coming out from the stem, and leaves and flowers are being seen on those branches, and these flowers are going to grow further. Becomes fruit. All these together make up the shoot system.
So, friends, we have studied roots completely, like what the Root is, what the root system is, how many types of roots there are, what modifications are made to the Root, the region of the Root, etc.
So, friends, I hope you have liked the information given about what roots are and what the function of roots is; if you like it, then share it on your social app.
Thank you