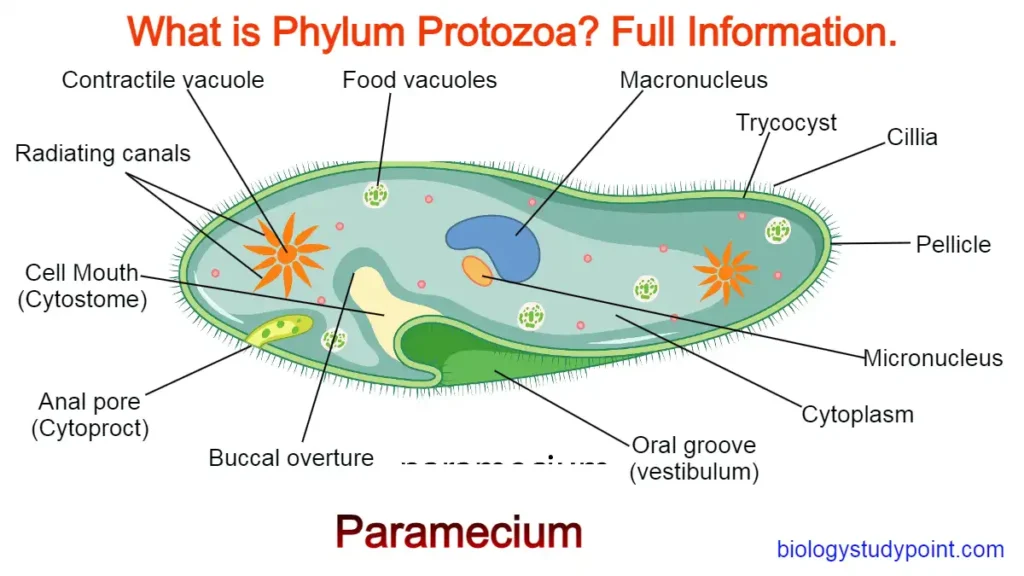
Hello friends, in this article where is the cytoskeleton found? Friends, in this article we will learn about the components and functions of the cytoskeleton, its presence in different types of cells, the history of cytoskeleton research, its role in diseases, and its potential as a therapeutic target.
Where is Cytoskeleton found?
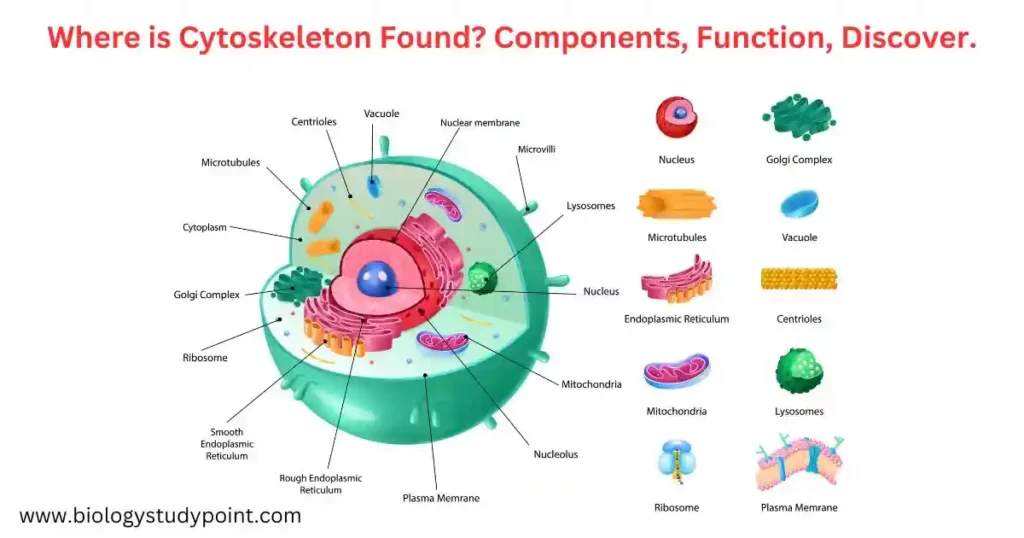
The cytoskeleton is an important and complex network of protein filaments found in eukaryotic cells, which helps maintain the shape of the cell and activates many cellular functions.
What is a Cytoskeleton?
A structure that provides protection to the cell and maintains its shape is called a cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton consists of protein fibers and is membrane-less and also helps the cell movements.
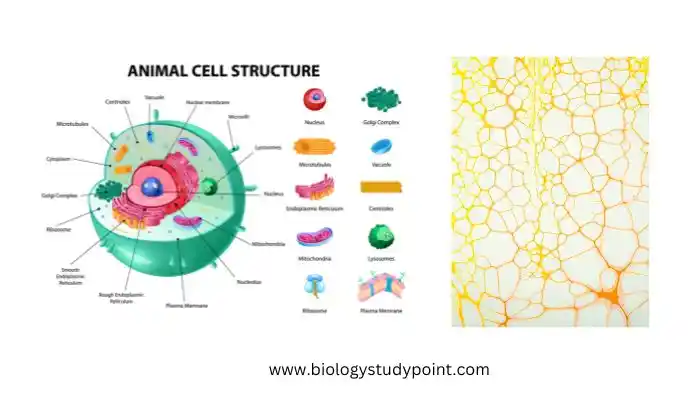
The skeletal system of the cell is called the cytoskeleton. It is found in all eukaryotic and various types of prokaryotic cells. It is in the form of a complex system of different types of fibers spread in the cytoplasm. These fibers are made of fibrous protein. The cytoskeleton provides structural support to the cell and helps in movement.
Components of Cytoskeleton –
Cytoskeletons are made up of three types of fibers.
- Microtubules
- Microfilaments
- Intermediate Filaments
What are microtubules?
These are hollow and cylindrical structures made up of subunits of tubulin protein. These are present in the ectoplasm just below the plasma membrane. Its diameter is 25 nm.
What is Microfilaments?
These are solid, thin filaments made of actin protein, which helps cell movement. These fibers are found in large numbers in muscle cells. Their diameter is 6-7 nm.
What are Intermediate Filaments?
These are strong, solid, and thread-like fibers made of different types of proteins with similar structures. These spread through the cytoplasm and are attached to microtubules. These fibers are not found in plant cells. These provide specific functions to particular types of tissue.
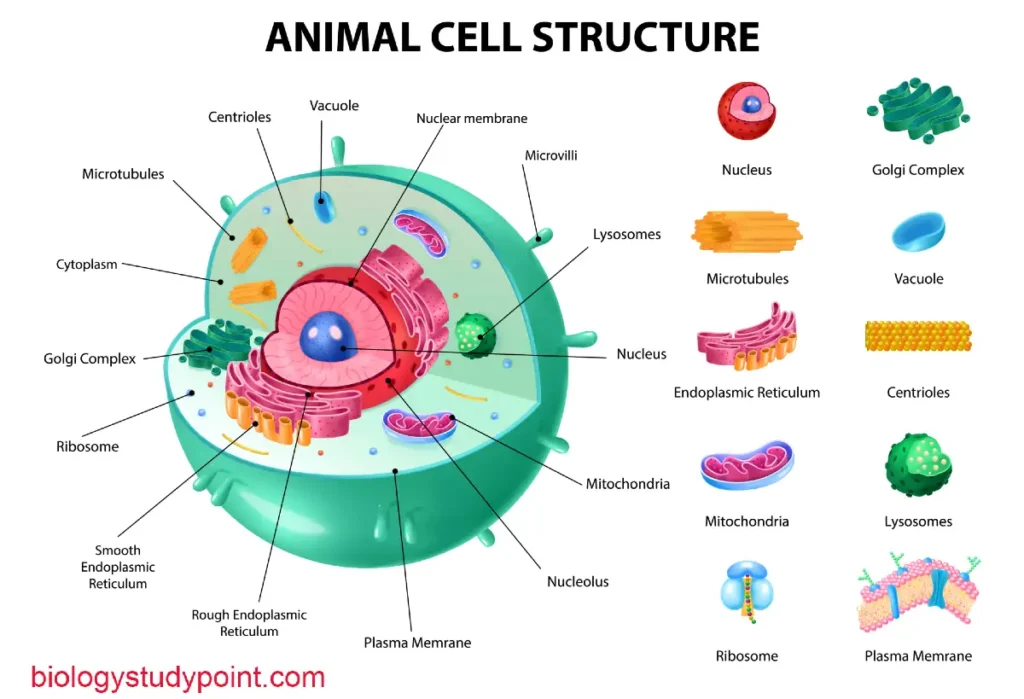
Cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells –
Cytoskeleton is most commonly seen in eukaryotic cells, which include both animal and plant cells.
Animal Cells –
In animal cells, the cytoskeleton is essential for muscle contraction and cell migration, as well as cell movement. It also maintains the shape of the cell and is important for cell division.
Plant cells –
In plant cells, the cytoskeleton plays a significant role in cell growth and maintaining the strength of the cell membrane.
Cytoskeleton in prokaryotic cells –
Friends, the cytoskeleton is studied the most in eukaryotic cells. Like bacteria, some prokaryotic cells also contain cytoskeleton elements that help in cell division and maintaining cell shape.
Research and Discoveries –
Research on the cytoskeleton has a long history. In 1993, Richard H. Scheller, James Rothman, and Randy Schekman were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on vesicle trafficking, which also involved the cytoskeleton.
Cytoskeleton in disease –
Looseness of the cytoskeleton can lead to many diseases. For example, mutations in genes encoding cytoskeleton proteins are associated with muscular dystrophy, a group of genetic disorders characterized by muscle weakness. Understanding the role of the cytoskeleton in diseases opens the doors to greater chances for therapeutic intervention.
Function of Cytoskeleton –
- Structural support – Friends, the cytoskeleton helps in maintaining the structure and shape of the cell.
- Internal framework — It forms the structure or framework inside the cell which works to maintain the position of various organelles within the cell.
- Movement of substances — Microfilaments and microfibrils establish part of the machinery needed for the movement of substances and organelles within the cell, such as transporting vesicles from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi and from the Golgi to the lysosome. Movement of chromosomes during cell division, formation of pinocytic or phagocytic vesicles, and movement of vesicles containing neurotransmitters along the length of nerve cells.
- Cell movement — The movement of single-celled organisms or cellular movement by some WBCs depends on the power-generating elements of the cytoskeleton.
- Protein synthesis – The translation system of the cell remains attached to the cytoskeleton. This means that it provides construction space to support mRNA and ribosomes.
- Signal transduction – The cytoskeleton contacts the inner surface of the plasma membrane and plays an important role in sending signals from the external environment to the cell interior.
Cytoskeleton and Cell Movements
Microtubules and cell movement –
Microtubules are part of the mitotic spindle, centrioles, and core structures or the axoneme of cilia and flagella. Therefore, microtubules are associated with the movement of chromosomes during cell division.
The microtubules composing the axoneme or core of the cilia and flagellum form the mechanical mechanism to generate the force necessary for movement. Cilia and flagella help unicellular organisms to swim and move.
Microfilaments –
Microfibers play a significant role in all types of contractions and movements inside the cell. Skeletal contraction of muscle fibers occurs by sliding of thin microfilaments containing actin. Friends Muscle contraction and relaxation, aids in movement and mobility.
Non-muscle movements and contractions –
It helps the cells to crawl to the base or bottom. This happens due to the presence of actin fibers. Pseudopodia formation and amoeboid movement occur due to the action of an actin microfibril. Actin microfibrils are present in the cytoplasm of the cell.
Changes in cell shape –
Changes in cell shape and cell movement during embryonic development at the end of gastrulation are caused by the concentration of a band of microfilaments. These gather in the cortical region of cells just beneath the outermost cell membrane, and their contraction pulls the cytoplasm in that direction.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the three main components of the cytoskeleton?
The three main components of the cytoskeleton are microfilaments, microtubules, and intermediate filaments.
How does the cytoskeleton function in cellular movement?
The cytoskeleton regulates cell movement by facilitating the contraction of muscle cells and through dynamic changes in its structure. Is responsible for cellular movement by allowing migration.
Can the cytoskeleton be found in prokaryotic cells?
Yes, some prokaryotic cells like bacteria also have cytoskeleton elements that are involved in cell division and maintaining cell shape.
Are there any diseases associated with cytoskeleton dysfunction?
Yes, mutations in genes encoding cytoskeleton proteins can cause diseases such as muscular dystrophy, which is characterized by muscle weakness.
How has research on the cytoskeleton contributed to scientific progress?
Cytoskeleton Research has led to a better understanding of cell biology and the development of treatments for diseases related to cytoskeleton dysfunction.
Conclusion –
Friends, I hope that the information given in this article about where is cytoskeleton found would have been helpful for you. If you find any mistake in it, then please do tell by commenting, with your comment we can correct our mistakes.
Thank you